mPEG-PAMAM-G4 nucleic acid nanocomplexes: enhanced stability, RNase protection, and activity of splice switching oligomer and poly I:C RNA
- PMID: 24164501
- PMCID: PMC4295786
- DOI: 10.1021/bm4012425
mPEG-PAMAM-G4 nucleic acid nanocomplexes: enhanced stability, RNase protection, and activity of splice switching oligomer and poly I:C RNA
Abstract
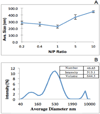
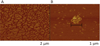
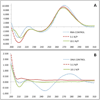
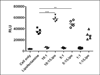
Dendrimer chemistries have virtually exploded in recent years with increasing interest in this class of polymers as gene delivery vehicles. An effective nucleic acid delivery vehicle must efficiently bind its cargo and form physically stable complexes. Most importantly, the nucleic acid must be protected in biological fluids and tissues, as RNA is extremely susceptible to nuclease degradation. Here, we characterized the association of nucleic acids with generation 4 PEGylated poly(amidoamine) dendrimer (mPEG-PAMAM-G4). We investigated the formation, size, and stability over time of the nanoplexes at various N/P ratios by gel shift and dynamic light scatter spectroscopy (DLS). Further characterization of the mPEG-PAMAM-G4/nucleic acid association was provided by atomic force microscopy (AFM) and by circular dichroism (CD). Importantly, mPEG-PAMAM-G4 complexation protected RNA from treatment with RNase A, degradation in serum, and various tissue homogenates. mPEG-PAMAM-G4 complexation also significantly enhanced the functional delivery of RNA in a novel engineered human melanoma cell line with splice-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs) targeting a recombinant luciferase transcript. mPEG-PAMAM-G4 triconjugates formed between gold nanoparticle (GNP) and particularly manganese oxide (MnO) nanorods, poly IC, an anticancer RNA, showed enhanced cancer-killing activity by an MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) cell viability assay.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Low systemic toxicity nanocarriers fabricated from heparin-mPEG and PAMAM dendrimers for controlled drug release.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018 Jan 1;82:291-298. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.07.051. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018. PMID: 29025661
-
Bundling and aggregation of DNA by cationic dendrimers.Biomacromolecules. 2011 Feb 14;12(2):511-7. doi: 10.1021/bm1013102. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Biomacromolecules. 2011. PMID: 21192723
-
Targeting Breast Cancer Cells with G4 PAMAM Dendrimers and Valproic Acid Derivative Complexes.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(15):1857-1872. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200423073812. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32324521
-
Review on the targeted conjugation of anticancer drugs doxorubicin and tamoxifen with synthetic polymers for drug delivery.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017 Aug;35(11):2497-2508. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2016.1222971. Epub 2016 Sep 6. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2017. PMID: 27598545 Review.
-
PEGylated PAMAM dendrimers: Enhancing efficacy and mitigating toxicity for effective anticancer drug and gene delivery.Acta Biomater. 2016 Oct 1;43:14-29. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.07.015. Epub 2016 Jul 12. Acta Biomater. 2016. PMID: 27422195 Review.
Cited by
-
Biocompatible FePO4 Nanoparticles: Drug Delivery, RNA Stabilization, and Functional Activity.Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021 Nov 27;16(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s11671-021-03626-8. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021. PMID: 34837559 Free PMC article.
-
Cationic Nanomaterials for Autoimmune Diseases Therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 21;12:762362. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.762362. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35126109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Cationic Carbosilane Dendrimers and Their siRNA Complexes with MCF-7 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7097. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137097. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281151 Free PMC article.
-
ZnO Nanoparticles Protect RNA from Degradation Better than DNA.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017 Nov 8;7(11):378. doi: 10.3390/nano7110378. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29117135 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Exchange Between Free and Bound States in RNA-Dendrimer Polyplexes: Implications on the Mechanism of Delivery and Release.Biomacromolecules. 2016 Jan 11;17(1):154-64. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01280. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Biomacromolecules. 2016. PMID: 26595195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Samad A, Alam IM, Saxena K. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009;15:2958–2969. - PubMed
-
- Patri AK, Majoros IJ, Baker JR., Jr Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002;6:466–471. - PubMed
-
- Lee CC, MacKay JA, Fréchet JMJ, Szoka FC. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23:1517–1526. - PubMed
-
- Liu N, Hao Y, Yin Z, Ma M, Wang L, Zhang X. Pharmazie. 2012;67:174–181. - PubMed
-
- Liu M, Fréchet JM. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today. 1999;2:393–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

