CD49a promotes T-cell-mediated hepatitis by driving T helper 1 cytokine and interleukin-17 production
- PMID: 24164540
- PMCID: PMC3930377
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12201
CD49a promotes T-cell-mediated hepatitis by driving T helper 1 cytokine and interleukin-17 production
Abstract
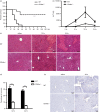
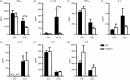
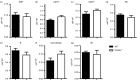
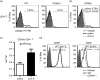
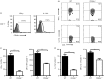
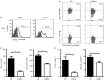
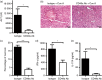
It is becoming increasingly clear that the T-cell-mediated immune response is important in many diseases. In this study, we used concanavalin A (Con A) -induced hepatitis to investigate the role of CD49a in the molecular and cellular mechanism of the T-cell-mediated immune response. We found that CD49a(-/-) mice had significantly reduced levels of serum alanine aminotransferase and were protected from Con A-induced hepatitis. CD49a deficiency led to decreased production of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and interleukin-17A (IL-17A) after Con A injection. Furthermore, we found that hepatic CD4(+) T cells and invariant natural killer T cells up-regulated CD49a expression, along with enhanced activation after Con A injection, leading to production of inflammatory cytokines by these T cells. Blockade of CD49a in vivo ameliorated Con A-induced hepatitis with reduced production of IFN-γ and IL-17A. Hence, CD49a promoted Con A-induced hepatitis through enhancing inflammatory cytokine production (IFN-γ and IL-17A) by CD4(+) T and invariant natural killer T cells. The protective effect of CD49a blockade antibody suggested a new target therapeutic molecule for intervention of T-cell-mediated liver injury.
Keywords: CD49a; T-cell-mediated hepatitis; interferon-γ; interleukin-17A.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Myeloid STAT3 inhibits T cell-mediated hepatitis by regulating T helper 1 cytokine and interleukin-17 production.Gastroenterology. 2009 Dec;137(6):2125-35.e1-2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.004. Epub 2009 Aug 15. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19686746 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury of mice by bacterial lipopolysaccharide via the induction of IL-6 and the subsequent reduction of IL-4: the cytokine milieu of concanavalin A hepatitis.J Hepatol. 1999 Jul;31(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80159-7. J Hepatol. 1999. PMID: 10424279
-
Toll-like receptor 5 signaling restrains T-cell/natural killer T-cell activation and protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury.Hepatology. 2017 Jun;65(6):2059-2073. doi: 10.1002/hep.29140. Epub 2017 May 4. Hepatology. 2017. PMID: 28273362
-
Vγ4 γδ T cell-derived IL-17A negatively regulates NKT cell function in Con A-induced fulminant hepatitis.J Immunol. 2011 Nov 15;187(10):5007-14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101315. Epub 2011 Oct 10. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21987663
-
γδ T cells are indispensable for interleukin-23-mediated protection against Concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice.Immunology. 2017 May;151(1):43-55. doi: 10.1111/imm.12712. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Immunology. 2017. PMID: 28092402 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Application of Concanavalin A during immune responsiveness skin-swelling tests facilitates measurement interpretation in mammalian ecology.Ecol Evol. 2016 Jun 10;6(13):4551-64. doi: 10.1002/ece3.2211. eCollection 2016 Jul. Ecol Evol. 2016. PMID: 27386096 Free PMC article.
-
Invariant NKT Cell-Mediated Modulation of ILC1s as a Tool for Mucosal Immune Intervention.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 7;10:1849. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01849. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31440243 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Viral Liver Diseases: Approaching the Liver Using T Cell Receptor-Mediated Gene Technologies.Cells. 2020 Jun 16;9(6):1471. doi: 10.3390/cells9061471. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32560123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adenovirus‑mediated knockdown of activin A receptor type 2A attenuates immune‑induced hepatic fibrosis in mice and inhibits interleukin‑17‑induced activation of primary hepatic stellate cells.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jul;42(1):279-289. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3600. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29620144 Free PMC article.
-
CD24 aggravates acute liver injury in autoimmune hepatitis by promoting IFN-γ production by CD4+ T cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2018 Mar;15(3):260-271. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2016.57. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Cell Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28065940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang S, Liang R, Luo W, et al. High susceptibility to liver injury in IL-27 p28 conditional knockout mice involves intrinsic interferon-γ dysregulation of CD4+ T cells. Hepatology. 2012;57:1620–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

