Stable micron-scale holes are a general feature of canonical holins
- PMID: 24164554
- PMCID: PMC4009996
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.12439
Stable micron-scale holes are a general feature of canonical holins
Abstract
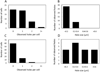
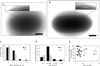
At a programmed time in phage infection cycles, canonical holins suddenly trigger to cause lethal damage to the cytoplasmic membrane, resulting in the cessation of respiration and the non-specific release of pre-folded, fully active endolysins to the periplasm. For the paradigm holin S105 of lambda, triggering is correlated with the formation of micron-scale membrane holes, visible as interruptions in the bilayer in cryo-electron microscopic images and tomographic reconstructions. Here we report that the size distribution of the holes is stable for long periods after triggering. Moreover, early triggering caused by an early lysis allele of S105 formed approximately the same number of holes, but the lesions were significantly smaller. In contrast, early triggering prematurely induced by energy poisons resulted in many fewer visible holes, consistent with previous sizing studies. Importantly, the unrelated canonical holins P2 Y and T4 T were found to cause the formation of holes of approximately the same size and number as for lambda. In contrast, no such lesions were visible after triggering of the pinholin S(21) 68. These results generalize the hole formation phenomenon for canonical holins. A model is presented suggesting the unprecedentedly large size of these holes is related to the timing mechanism.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Micron-scale holes terminate the phage infection cycle.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 2;107(5):2219-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914030107. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20080651 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the structure of the S105 hole.J Bacteriol. 2014 Nov;196(21):3683-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01673-14. Epub 2014 Aug 4. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 25092029 Free PMC article.
-
The pinholin of lambdoid phage 21: control of lysis by membrane depolarization.J Bacteriol. 2007 Dec;189(24):9135-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00847-07. Epub 2007 Sep 7. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17827300 Free PMC article.
-
[Current advance in the topological structure and function of holin encoded by bacteriophage lambda--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2012 Feb 4;52(2):141-5. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22586990 Review. Chinese.
-
Holin of bacteriophage lambda: structural insights into a membrane lesion.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Aug;69(4):781-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06335.x. Epub 2008 Jun 28. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18573181 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic dissection of T4 lysis.J Bacteriol. 2014 Jun;196(12):2201-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.01548-14. Epub 2014 Apr 4. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24706740 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Basis for Escherichia coli O157:H7 Phage FAHEc1 Endolysin Function and Protein Engineering to Increase Thermal Stability.Viruses. 2021 Jun 9;13(6):1101. doi: 10.3390/v13061101. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34207694 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Analysis of the Lambda Spanins Rz and Rz1: Identification of Functional Domains.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Feb 9;7(2):741-753. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.037192. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28040784 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and assembly mechanism of virus-associated pyramids.Biophys Rev. 2018 Apr;10(2):551-557. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0357-4. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 29204884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The short cytoplasmic region of phage T4 holin is essential for the transition from impermeable membrane protein complexes to permeable pores.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 30;16:1579756. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1579756. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40520373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhya S, Sen A, Mitra S, Hershey AD. The Bacteriophage Lambda. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1971. The role of gene S; pp. 743–746.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

