Kyphoplasty increases vertebral height, decreases both pain score and opiate requirements while improving functional status
- PMID: 24165285
- PMCID: PMC3949154
- DOI: 10.1111/papr.12131
Kyphoplasty increases vertebral height, decreases both pain score and opiate requirements while improving functional status
Abstract
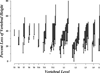
Vertebral compression fractures can result from advanced osteoporosis, or less commonly from metastatic or traumatic insults to the vertebral column, and result in disabling pain and decreased functional capacity. Various vertebral augmentation options including kyphoplasty aim at preventing the sequelae of pain and immobility that can develop as the result of the vertebral fractures. The mechanism for pain relief following kyphoplasty is not entirely understood, and the restoration of a portion of the lost vertebral height is a subject of debate. We retrospectively reviewed radiographic imaging, pain relief, analgesic intake and functional outcomes in 67 consecutive patients who underwent single- or multilevel kyphoplasty with the primary goal of quantifying the restoration of lost vertebral height. We observed a mean of 45% of the lost vertebral height restored postprocedurally. Secondarily, kyphoplasty was associated with significant decreases in pain scores, daily morphine consumption and improvement in patient-reported functional measures.
Keywords: kyphoplasty; kyphosis; osteoporosis; percutaneous vertebral augmentation; vertebral compression fracture; vertebral height restoration.
© 2013 World Institute of Pain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Beyond Pain Relief: An In-Depth Review of Vertebral Height Restoration After Balloon Kyphoplasty in Vertebral Compression Fractures.Cureus. 2023 Sep 28;15(9):e46124. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46124. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37900521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional outcomes and height restoration for patients with multiple myeloma-related osteolytic vertebral compression fractures treated with kyphoplasty.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014 Aug;27(6):342-6. doi: 10.1097/BSD.0b013e318260a076. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014. PMID: 22668752
-
Is there a stable vertebral height restoration with the new radiofrequency kyphoplasty? A clinical and radiological study.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013 Jul;23(5):507-13. doi: 10.1007/s00590-012-1026-8. Epub 2012 Jun 30. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013. PMID: 23412159
-
A prospective, international, randomized, noninferiority study comparing an implantable titanium vertebral augmentation device versus balloon kyphoplasty in the reduction of vertebral compression fractures (SAKOS study).Spine J. 2019 Nov;19(11):1782-1795. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 31325625 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of radiological and clinical results of balloon kyphoplasty according to anterior height loss in the osteoporotic vertebral fracture.Spine J. 2014 Oct 1;14(10):2281-9. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2014.01.028. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24462536
Cited by
-
Complications and healthcare utilization in commercially-insured osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture patients: a comparison of kyphoplasty versus propensity-matched controls.Spine J. 2021 Aug;21(8):1347-1354. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.03.025. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Spine J. 2021. PMID: 33781968 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical effect of different vertebral body height restoration rates after percutaneous kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Sep 5;25(1):711. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07773-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39237984 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Pain Relief: An In-Depth Review of Vertebral Height Restoration After Balloon Kyphoplasty in Vertebral Compression Fractures.Cureus. 2023 Sep 28;15(9):e46124. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46124. eCollection 2023 Sep. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37900521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk factors of residual back pain after vertebral augmentation in osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jul 25;26(1):702. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08945-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40713499 Free PMC article.
-
Cementless fixation of osteoporotic VCFs using titanium mesh implants (OsseoFix): preliminary results.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:853897. doi: 10.1155/2014/853897. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25110699 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Riggs BL, Melton LJ. The worldwide problem of osteoporosis: insights afforded by epidemiology. Bone. 1995;17:505S–511S. - PubMed
-
- Felsenberg D, Silman AJ, et al. European Prospective Osteoporosis Study (EPOS) Group. Incidence of vertebral fracture in Europe: results from the European Prospective Osteoporosis Study (EPOS) J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17:716–724. - PubMed
-
- Johnell O, Kanis JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporosis Int. 2006;17:1726–1733. - PubMed
-
- Ross PD, Davis JW, Epstein RS, Wasnich RD. Preexisting fractures and bone mass predict vertebral fracture incidence in women. Ann Intern Med. 1991;114:919–923. - PubMed
-
- Schlaich C, Minne HW, Bruckner T, et al. Reduced pulmonary function in patients with spinal osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporosis Int. 1998;8:261–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

