Repulsive guidance cue semaphorin 3A in urine predicts the progression of acute kidney injury in adult patients from a mixed intensive care unit
- PMID: 24166457
- PMCID: PMC3888311
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gft414
Repulsive guidance cue semaphorin 3A in urine predicts the progression of acute kidney injury in adult patients from a mixed intensive care unit
Abstract
Backgrounds: Predicting the development of acute kidney injury (AKI) in the critical care setting is challenging. Although several biomarkers showed somewhat satisfactory performance for detecting established AKI even in a heterogeneous disease-oriented population, identification of new biomarkers that predict the development of AKI accurately is urgently required.
Methods: A single-center prospective observational cohort study was undertaken to evaluate for the first time the reliability of the newly identified biomarker semaphorin 3A for AKI diagnosis in heterogeneous intensive care unit populations. In addition to five urinary biomarkers of L-type fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), IL-18, albumin and N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase (NAG), urinary semaphorin 3A was measured at intensive care unit (ICU) admission.
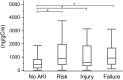
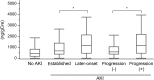
Results and conclusion: Three hundred thirty-nine critically ill adult patients were recruited for this study. Among them, 131 patients (39%) were diagnosed with AKI by the RIFLE criteria and 66 patients were diagnosed as AKI at post-ICU admission (later-onset AKI). Eighty-four AKI patients showed worsening severity during 1 week observation (AKI progression). Although L-FABP, NGAL and IL-18 showed significantly higher area under the curve (AUC)-receiver operating characteristic (ROC) values than semaphorin 3A in detecting established AKI, semaphorin 3A was able to detect later-onset AKI and AKI progression with similar AUC-ROC values compared with the other five biomarkers [AUC-ROC (95% CI) for established AKI 0.64 (0.56-0.71), later-onset AKI 0.71 (0.64-0.78), AKI progression 0.71 (0.64-0.77)]. Urinary semaphorin 3A was not increased in non-progressive established AKI, while the other biomarkers were elevated regardless of further progression. Finally, sepsis did not have any impact on semaphorin 3A while the other urinary biomarkers were increased with sepsis. Semaphorin 3A is a new biomarker of AKI which may have a distinct predictive use for AKI progression when compared with other AKI biomarkers.
Keywords: AKI progression; acute kidney injury; biomarker; mixed ICU; semaphorin 3A.
Figures

References
-
- Hirsch R, Dent C, Pfriem H, et al. NGAL is an early predictive biomarker of contrast-induced nephropathy in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:2089–2095. - PubMed
-
- Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005;365:1231–1238. - PubMed
-
- Parikh CR, Jani A, Mishra J, et al. Urine NGAL and IL-18 are predictive biomarkers for delayed graft function following kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2006;6:1639–1645. - PubMed
-
- Parikh CR, Mishra J, Thiessen-Philbrook H, et al. Urinary IL-18 is an early predictive biomarker of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Kidney Int. 2006;70:199–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

