Urodynamic studies for management of urinary incontinence in children and adults
- PMID: 24166676
- PMCID: PMC6599826
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003195.pub3
Urodynamic studies for management of urinary incontinence in children and adults
Abstract
Background: Urodynamic tests are used to investigate people who have urinary incontinence or other urinary symptoms in order to make a definitive, objective diagnosis. The aim is to help select the treatment most likely to be successful. The investigations are invasive and time consuming.
Objectives: The objective of this review was to determine if treatment according to a urodynamic-based diagnosis, compared to treatment based on history and examination, led to more effective clinical care of people with urinary incontinence and better clinical outcomes.The intention was to test the following hypotheses in predefined subgroups of people with incontinence:(i) urodynamic investigations improve the clinical outcomes;(ii) urodynamic investigations alter clinical decision making;(iii) one type of urodynamic test is better than another in improving the outcomes of management of incontinence or influencing clinical decisions, or both.
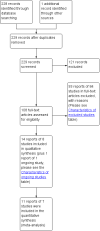
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Incontinence Group Specialised Register, which contains trials identified from the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE and MEDLINE In-Process, handsearching of journals and conference proceedings (searched 19 February 2013), and the reference lists of relevant articles.
Selection criteria: Randomised and quasi-randomised trials comparing clinical outcomes in groups of people who were and were not investigated using urodynamics, or comparing one type of urodynamic test against another were included. Trials were excluded if they did not report clinical outcomes.
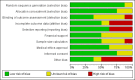
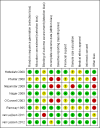
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted data.
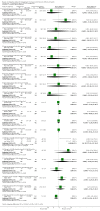
Main results: Eight trials involving around 1100 people were included but data were only available for 1036 women in seven trials, of whom 526 received urodynamics. There was some evidence of risk of bias. The four deaths and 12 dropouts in the control arm of one trial were unexplained.There was significant evidence that the tests did change clinical decision making. Women in the urodynamic arms of three trials were more likely to have their management changed (proportion with change in management compared with the control arm 17% versus 3%, risk ratio (RR) 5.07, 95% CI 1.87 to 13.74), although there was statistical heterogeneity. There was evidence from two trials that women treated after urodynamic investigations were more likely to receive drugs (RR 2.09, 95% CI 1.32 to 3.31). On the other hand, in five trials women undergoing treatment following urodynamic investigation were not more likely to undergo surgery (RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.12).There was no statistically significant difference however in the number of women with urinary incontinence if they received treatment guided by urodynamics (37%) compared with those whose treatment was based on history and clinical findings alone (36%) (for example, RR for the number with incontinence after the first year 1.02, 95% CI 0.86 to 1.21). It was calculated that the number of women needed to treat was 100 women (95% CI 86 to 114 women) undergoing urodynamics to prevent one extra individual being incontinent at one year.One trial reported adverse effects and no significant difference was found (RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.81 to 1.50).
Authors' conclusions: While urodynamic tests did change clinical decision making, there was some evidence that this did not result in better outcomes in terms of a difference in urinary incontinence rates after treatment. There was no evidence about their use in men, children, or people with neurological diseases. Larger definitive trials are needed in which people are randomly allocated to management according to urodynamic findings or to management based on history and clinical examination to determine if performance of urodynamics results in higher continence rates after treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures











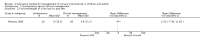






Update of
-
Urodynamic studies for management of urinary incontinence in children and adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD003195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003195.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Oct 29;(10):CD003195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003195.pub3. PMID: 22258952 Updated.
Comment in
-
Re: Urodynamic Studies for Management of Urinary Incontinence in Children and Adults: A Short Version Cochrane Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Urol. 2015 Aug;194(2):473-4. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.05.068. Epub 2015 May 18. J Urol. 2015. PMID: 26195387 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Holtedahl 2000 {published data only}
-
- Holtedahl K, Verelst M, Schiefloe A, Hunskaar S. Usefulness of urodynamic examination in female urinary incontinence‐‐lessons from a population‐based, randomized, controlled study of conservative treatment. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology 2000;34(3):169‐74. [SR‐INCONT11839] - PubMed
Khullar 2000 {published data only}
-
- Khullar V, Salvatore S, Cardozo L, Howland E, Digesu A, Kelleher C, et al. Randomised study of ambulatory urodynamics versus symptomatic treatment of symptomatic women without a urodynamic diagnosis. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 30th Annual Meeting; 2000 Aug 28‐31; Tampere, Finland. 2000.
Majumdar 2009 {published data only}
-
- Majumdar A, Hassan I, Robb K, Toozs‐Hobson P. Urodynamics and patient preference (Abstract number 366). Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Continence Society (ICS), 2005 Aug 28 ‐ Sept 2; Montreal. 2005. [21078]
-
- Majumdar A, Latthe P, Toozs‐Hobson P. Urodynamics prior to treatment as an intervention: A pilot study. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2010;29(4):522‐6. [SR‐INCONT34191] - PubMed
-
- Majumdar A, Toozs‐Hobson P. Why women prefer to have urodynamics (Abstract number 11). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2007;26(5):615‐6. [26653]
-
- Toozs‐Hobson P, Majundar A, Robb K, Powles K. How does urodynamics affect subsequent patient behaviour? (Abstract number 159). International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2007;18 Suppl 1:S94‐5. [26604]
Nager 2009 {published data only}
-
- Sirls L, Richter H, Litman H, Kenton K, Lemack G, Lukacz E, et al. The effect of urodynamic testing on clinical diagnosis, treatment plan and outcomes in women undergoing stress urinary incontinence surgery (Abstract number 251). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2012;31(6):1051‐2. [SR‐INCONT45980] - PMC - PubMed
O'Connell 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dowling CR, O'Connell HE, Kurczyki L, Myles K, Poole K, Sanjeevan KV. Randomised control trial of bladder pressure management versus management based on symptoms and residual volumes in patients with established multiple sclerosis (Abstract). BJU International 2005;95 Suppl 1:5. [21317]
-
- O'Connell HE, Costello AJ, King J, Kilpatrick T, Whishaw M, Samali R, et al. Extension study: Randomised control trial bladder pressure management vs management based on symptoms and residual volumes in patients with established multiple sclerosis. Canberra, Australia: National Continence Management Strategy, Department of Health and Ageing, Australian Government, 2005. Available from: http://www.bladderbowel.gov.au/ncms/projects/intervention/msurinarprob.htm. [31113]
-
- O'Connell HE, Costello AJ, King J, Kilpatrick T, Whishaw M, Samali R, et al. Randomised control trial bladder pressure management vs management based on symptoms and residual volumes in patients with established multiple sclerosis. Canberra, Australia: National Continence Management Strategy, Department of Health and Ageing, Australian Government, 2003. Available from: http://www.bladderbowel.gov.au/ncms/projects/phases/bladder%20pressure.htm. [31112]
Ramsay 1995 {published data only}
-
- Ramsay I, Hassan A, Hunter M, Donaldson K. A randomised controlled trial of urodynamic investigation prior to conservative treatment of urinary incontinence in the female (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 1994;13(4):455‐6.
-
- Ramsay IN, Ali HM, Hunter M, Stark D, Donaldson K. A randomized controlled trial of urodynamic investigations prior to conservative treatment of urinary incontinence in the female. International Urogynecology Journal 1995;6:277‐81. - PubMed
van Leijsen 2011 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Leijsen SA, Kluivers KB, Mol BW, Broekhuis SR, Milani AL, Bongers MY, et al. A randomized controlled trial on the value of preoperative urodynamic investigation in women with stress incontinence (Abstract number 165) [nb use version sent by first author as published version has wrong RRs]. International Urogynaecology Journal 2011;22(1 Suppl):S158‐60. [SR‐INCONT45788]
-
- Leijsen SA, Kluivers KB, Mol BW, Broekhuis SR, Milani AL, Bongers MY, et al. Can preoperative urodynamic investigation be omitted in women with stress urinary incontinence? A non‐inferiority randomized controlled trial. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2012;31(7):1118‐23. [SR‐INCONT45113] - PubMed
-
- Leijsen SAL, Kluivers KB, Mol BWJ, Broekhuis SR, Milani AL, Bongers MY, et al. A randomised controlled trial on the value of preoperative urodynamics in women with stress incontinence: VUSIS 1 [Abstract 165]. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2011;22 Suppl 1:S159‐61.
van Leijsen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Leijsen S, Kluivers KB, Mol BW, Milani A, Roovers J, Boon J, et al. A randomised controlled trial on the value of urodynamics prior to stress incontinence surgery (Abstract number 248). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2012;31(6):1046‐7. [SR‐INCONT45979]
-
- Leijsen SA, Kluivers KB, Mol BW, Broekhuis SR, Milani FL, Vaart CH, et al. Protocol for the value of urodynamics prior to stress incontinence surgery (VUSIS) study: a multicenter randomized controlled trial to assess the cost effectiveness of urodynamics in women with symptoms of stress urinary incontinence in whom surgical treatment is considered. BMC Women's Health 2009;9:22. [SR‐INCONT32078] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leijsen SAL, Kluivers KB, Mol BWJ, in 't Hout J, Milani AL, Roovers JPWR, et al. Value of urodynamics before stress urinary incontinence surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2013;121(5):999‐1008. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Akil 2005 {published data only}
-
- Akil I, Ozkol M, Ikizoglu OY, Polat M, Tuncyurek OY, Taskin O, et al. Premedication during micturating cystourethrogram to achieve sedation and anxiolysis. Pediatric Nephrology (Berlin, Germany) 2005;20(8):1106‐10. - PubMed
Bael 2008 {published data only}
-
- Bael A, Lax H, Hoebeke P, Jong TPVM, Nijman RJM, Sixt R, et al. The relevance of urodynamic studies in urge syndrome and dysfunctional voiding: a multi‐center controlled trial in children. Journal of Urology 2008;180(4):1486‐93. - PubMed
Bajpai 1982 {published data only}
-
- Bajpai M, Sutherst J, Brown M. Comparison of cystomat and multichannel cystometry in the diagnosis of bladder instability (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 12th Annual Meeting; 1982; Leiden, Germany. 1982:203‐4.
Baker 1991 {published data only}
-
- Baker KR, Drutz HP, Barnes MD. Effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis in preventing bacteriuria after multichannel urodynamic investigations: a blind, randomized study in 124 female patients. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1991;165(3):679‐81. - PubMed
Batista 1998 {published data only}
-
- Batista JE, Arano P, Granda M, Puigpelat T, Garat JM, Bauer S. Filling rate during cystometry: its effect on detrusor instability and compliance in children (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), Annual Meeting. 1998:144.
Baumann 2007 {published data only}
-
- Baumann BM, McCans K, Stahmer SA, Leonard MB, Shults J, Holmes WC. Caregiver and health care provider satisfaction with volumetric bladder ultrasound. Academic Emergency Medicine 2007;14(10):903‐7. [26374] - PubMed
Benson 1991 {published data only}
-
- Benson JT. Anatomic vs urodynamic evaluation of women with urinary incontinence (Abstract). Proceedings of the American Urogynecology Society, 12th Annual Meeting; 1991 Oct 23‐26; Newport Beach, California, USA. 1991.
Bhatia 1985 {published data only}
-
- Bhatia NN, Bergman A. Antibiotic prophylaxis following instrumentation of the urinary tract (Abstract). Proceedings of the American Urogynecology Society, 6th Annual Meeting; 1985 Nov 6‐9; San Diego, California. 1985.
Blaivas 2001 {published data only}
-
- Blaivas JG, Groutz A, Verhaaren M. Does the method of cystometry affect the incidence of involuntary detrusor contractions? A prospective randomized urodynamic study. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2001;20(2):141‐5. - PubMed
Bo 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bo K, Borstad E. Urodynamic assessment during pelvic floor muscle and transversus abdominis contraction (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 33rd Annual Meeting; 2003 Oct 5‐9; Florence. 2003:484‐5.
Byrne 1991 {published data only}
-
- Byrne P. A comparison of rectal and vaginal placement of abdominal pressure catheters during cystometry ‐ patient preference (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 21st Annual Meeting; 1991; Hannover, Federal Republic of Germany. 1991:49‐50.
Chin‐Peuckert 2004 {published data only}
-
- Chin‐Peuckert L, Rennick JE, Jednak R, Capolicchio JP, Salle JL. Should warm infusion solution be used for urodynamic studies in children? A prospective randomized study. Journal of Urology 2004;172(4 Pt 2):1657‐61. [SR‐INCONT19217] - PubMed
Choe 2001 {published data only}
-
- Choe JM. Sling surgery performed with and without preoperative urodynamics: a comparative outcomes analysis (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 31st Annual Meeting; 2001 Sept 18‐21; Seoul, Korea. 2001:Abstract 175.
Chung 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chung S, Lim R, Goldman RD. Intranasal fentanyl versus placebo for pain in children during catheterization for voiding cystourethrography. Pediatric Radiology 2010 Jul;40(7):1236‐40. - PubMed
Colstrup 1982 {published data only}
-
- Colstrup H, Andersen JT, Walter S. Detrusor reflex instability in the male. Fact or artefact? The influence of investigative technique on the frequency of detrusor instability in CO2‐cystometry (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 12th Annual Meeting; 1992; Leiden, Germany. 1982:201‐2.
Constatini 20148 {published data only}
-
- Constantini E, Mearini L, Biscotto S, Giannantoni A, Bini V, Porena M. Impact of different sized catheters on pressure‐flow studies in women with lower urinary tract symptoms. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2005;24(2):106‐10. [SR‐INCONT20148] - PubMed
Culligan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Culligan PJ, Goldberg RP, Blackhurst DW, Sasso K, Koduri S, Sand PK. Comparison of microtransducer and fiberoptic catheters for urodynamic studies. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2001;98(2):253‐7. - PubMed
Cundiff 1999 {published data only}
-
- Cundiff GW, McLennan MT, Bent AE. Randomized trial of antibiotic prophylaxis for combined urodynamics and cystourethroscopy. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1999 May;93(5 Pt 1):749‐52. - PubMed
Darouiche 1994 {published data only}
-
- Darouiche RO, Smith MS, Markowski J. Antibiotic prophylaxis for urodynamic testing in patients with spinal cord injury: a preliminary study. Journal of Hospital Infection 1994;28(1):57‐61. - PubMed
Dolan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Dolan LM, Dixon WE, Brown K, Ord T, Hilton P. Randomized comparison of vaginal and rectal measurement of intra‐abdominal pressure during subtracted dual‐channel cystometry. Urology 2005;65(6):1059‐63. - PubMed
Dompeyre 2007 {published data only}
-
- Dompeyre P, Fritel X, Bader G, Delmas V, Fauconnier A. Bladder sensitivity testing using a visual analogue scale: comparative cystometric study on women. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2007;26(3):350‐5. [SR‐INCONT23235] - PubMed
Eggersmann 1996 {published data only}
-
- Eggersmann C, Wienhold D, Dahms S, Schultz‐Lampel D, Thuroff JW. Influence of different lubricants to urodynamic evaluations. Proceedings of the International Continence Society, 26th Annual Meeting; 1996 Aug 27‐30; Athens, Greece. 1996:440‐1.
Gehrich 2012 {published data only}
-
- Gehrich AP, Hill MJ, McWilliams GD, Larsen W, McCartin T. Comparison of urodynamic volume measurements using room and body temperature saline: a double‐blinded randomized crossover study design. Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery 2012 May;18(3):170‐4. - PubMed
Gluck 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gluck T, Wagg A, Fry C, Malone‐Lee J. The effects of biochemical changes to filling media during urodynamic testing in women with lower urinary tract symptoms (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(4):355. - PubMed
Goodman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Goodman TR, Kilborn T, Pearce R. Warm or cold contrast medium in the micturating cystourethrogram (MCUG): which is best?. Clinical Radiology 2003;58(7):551‐4. - PubMed
Groutz 2000 {published data only}
-
- Groutz A, Blaivas JG, Verhaaren M. Does the method of cystometry affect the incidence of involuntary detrusor contractions? A prospective randomized urodynamic study (Abstract number 1169). Journal of Urology 2000;163(4 Suppl):263. [SR‐INCONT29635] - PubMed
Gurbuz 2011 {published data only}
-
- Gurbuz C, Guner B, Atis G, Canat L, Caskrulu T. The effectiveness of fosfomycin tromethamine and ciprofloxacin prophylaxis in preventing bacteriuria caused by urodynamic study, do patients need prophylaxis (Abstract number 894). Proceedings of the 41st Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 2011 Aug 29 to Sept 2, Glasgow, Scotland. 2011.
Handa 1994 {published data only}
-
- Handa VL, Jensen JK, Ostergard DR. The effect of patient position on urethral mobility (Abstract). Proceedings of the American Urogynecology Society, 15th Annual Scientific Meeting; 1994 Sept 21‐24; Toronto, Ontario. 1994:Abstract P10.
Heslington 1996 {published data only}
-
- Heslington K, Hilton P. Ambulatory monitoring and conventional cystometry in asymptomatic female volunteers [see comments]. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1996;103(5):434‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hirakauva 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hirakauva E, Kajikawa M, Falco K, Zucchi E, Castro R, Sartori MGF, et al. The prophylactic antibiotic therapy prevents lower urinary tract infection after the urodynamic test? (Abstract number 819). Proceedings of the Joint Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS) and the International Urogynecological Association, 2010 Aug 23‐27, Toronto, Canada. 2010.
Hosker 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hosker GL, Bryant AM, Wright G, Kilcoyne PM, Lord JC, Smith ARB. A comparison of normal saline and urografin 150 for cystometry in women (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 29th Annual Meeting; 1999; Denver, Colorado. 1999:420‐1.
Hougardy 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hougardy V, Vandeweerd JM, Reda AA, Foidart JM. The impact of detailed explanatory leaflets on patient satisfaction with urodynamic consultation: a double‐blind randomized controlled trial. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2009;28(5):374‐9. [SR‐INCONT32112] - PubMed
Hundley 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hundley AF, Brown MB, Brubaker L, Cundiff GW, Kreder K, Lotze P, et al. A multicentered comparison of measurements obtained with microtip and external water pressure transducers. International Urogynecology Journal 2006;17(4):400‐6. [SR‐INCONT22307] - PubMed
Jolic 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jolic V, Gilja I. Vaginal vs. transabdominal ultrasonography in the evaluation of female urinary tract anatomy, stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organs static disturbances. Zentralblatt fur Gynakologie 1997;119(10):483‐91. - PubMed
Kartal 2002 {published data only}
-
- Klausner AP, Galea J, Vapnek JM. Effect of catheter size on urodynamic assessment of bladder outlet obstruction. Urology 2002;60(5):875‐80. [SR‐INCONT15592] - PubMed
Keidan 2005 {published data only}
-
- Keidan I, Zaslansky R, Weinberg M, Ben Shlush A, Jacobson JM, Augarten A, et al. Sedation during voiding cystourethrography: comparison of the efficacy and safety of using oral midazolam and continuous flow nitrous oxide. The Journal of Urology 2005;174(4 Pt 2):1598‐1600, discussion 1601. [SR‐INCONT21987] - PubMed
Khan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Khan MS, Chaliha C, Leskova L, Khullar V. The relationship between urinary symptom questionnaires and urodynamic diagnoses: an analysis of two methods of questionnaire administration. BJOG 2004 May;111(5):468‐74. - PubMed
Khullar 1996 {published data only}
-
- Khullar V, Cardozo LD, Salvatore S, Hill S. Ultrasound: a noninvasive screening test for detrusor instability. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1996;103(9):904‐8. - PubMed
Khullar 2002 {published data only}
-
- Khullar V, Soligo M, Salvatore S. Does rectal distension alter bladder function? (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(4):354. [14543]
Klarskov 2009 {published data only}
-
- Klarskov N, Scholfield D, Soma K, Darekar A, Mills I, Lose G. Measurement of urethral closure function in women with stress urinary incontinence. Journal of Urology 2009 Jun;181(6):2628‐33. - PubMed
Kristjansson 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kristjansson B. A randomised evaluation of routine urodynamics in patients with LUTS [abstract]. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology Supplementum 1999;33 Suppl 200:9. [23728]
Kuhn 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kuhn A, Nager CW, Hawkins E, Schulz J, Stanton SL. A comparative study of water perfusion catheters and microtip transducer catheters for urethral pressure measurements. International Urogynecology Journal 18;8:931‐5. [SR‐INCONT23895] - PubMed
Kulseng 1995 {published data only}
-
- Kulseng‐Hanssen S, Kristoffersen M, Larsen E. Physiological bladder filling with 2 and 4 hours recording versus 45 minutes recording with 300 ml saline bladder prefilling using ambulatory urodynamic equipment (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 25th Annual Meeting; 1995; Sydney, Australia. 1995:151‐2.
Lee 2002 {published data only}
-
- Lee F, Susser J, Mundy A, Foxall P, Craggs M. Does urinary sodium affect bladder sensations in patients with an overactive bladder during urodynamics? (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 32nd Annual Meeting; 2002 Aug 28‐30; Heidelberg, Germany. 2002:102‐3 (Abstract 181).
Lucas 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lucas M, Moore K, Borkowski T, Pantuck A, Heesakkers J, Radziszewski P. Accuracy of CaptiFlow portable home flow measuring device and its use as a diagnostic tool in the management of LUTS ‐ a randomised cross over study (Abstract number 400). Proceedings of the 39th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 2009 Sep 29 ‐ Oct 3, San Francisco, CA. 2009. [SR‐INCONT35613]
Malone‐Lee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Malone‐Lee JG, Al Buheissi S. Does urodynamic verification of overactive bladder determine treatment success? Results from a randomized placebo‐controlled study. BJU International 2009 Apr;103(7):931‐7. - PubMed
Massey 1987 {published data only}
-
- Massey A, Howell S, Lewis P, Tribe B. Urethral profilometry by different methods (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 17th Annual Meeting; 1987 Sept; Bristol, UK. 1987:122‐3.
Medina 2002 {published data only}
-
- Medina C, Fynes M, Gold R, Wang K, Stanton S. Does the order of patient position for sequential bladder filling at cystometry influence observed detrusor activity? (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 32nd Annual Meeting; 2002 Aug 28‐30; Heidelberg, Germany. 2002:87‐8 (Abstract 162).
Medina 2005 {published data only}
-
- Medina CA, Takacs P. Shortening the process of determining postvoid residual. International Journal of Gynaecology and Obstetrics 2005;91(3):266‐7. [21868] - PubMed
Minardi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Minardi D, d'Anzeo G, Parri G, Polito M Jr, Piergallina M, Asmar Z. The role of uroflowmetry biofeedback and biofeedback training of the pelvic floor muscles in the treatment of recurrent urinary tract infections in women with dysfunctional voiding: a randomized controlled prospective study. Urology 2010;75(6):1299‐304. [SR‐INCONT39965] - PubMed
Mouritsen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Mouritsen L, Sander P, Bernstein I, Bach A. Comparison of palpation, ultrasonography and perineometry for examination of the pelvic floor. International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 1999;10 Suppl 1:S16‐7.
Mueller 2007 {published data only}
-
- Mueller ER, Kenton K, Mahajan S, FitzGerald MP, Brubaker L. Urodynamic prolapse reduction alters urethral pressure but not filling or pressure flow parameters. Journal of Urology 2007;177(2):600‐3. [SR‐INCONT22546] - PubMed
Neal 1987 {published data only}
-
- Neal DE, Rao CV, Styles RA, Ng T, Ramsden PD. Effects of catheter size on urodynamic measurements in men undergoing elective prostatectomy. British Journal of Urology 1987;60(1):64‐8. [544] - PubMed
Panayi 2008 {published data only}
-
- Panayi D, Khullar V, Spiteri M, Hendricken C, Fernando R. Randomised study to determine if rectal distension alters urodynamic findings? (Abstract number 57). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2008;27(7):636.
Payne 2001 {published data only}
-
- Payne CK, Sirinian E, Azevedo K. Effect of physiologic levels of urinary potassium on interstitial cystitis symptoms. Urology 2001;57 Suppl 6A:124. - PubMed
Peschers 2001 {published data only}
-
- Peschers UMK. Antibiotic treatment to prevent urinary tract infections after urodynamic evaluation. International Urogynecology Journal 2001;12(4):254‐7. - PubMed
Peters‐Gee 2003 {published data only}
-
- Peters‐Gee J, McKinney T, Rezapour M, Mastropietro M, Lucente V, Slack M, et al. Multicenter study of gynecare MoniTorr urethral resistance pressure versus standard urodynamic MEA. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;101(4 Suppl):114S. [17196]
Philip 2007 {published data only}
-
- Philip J, Irwin P. A double‐blind, randomised controlled trial of cystometry using normal saline versus 3M potassium chloride infusion (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (34th Annual Meeting) and the International UroGynecological Association; 2004 Aug 23‐27; Paris. 2004:Abstract number 739. [19085]
-
- Philip J, Willmott S, Irwin P. Interstitial cystitis versus detrusor overactivity: a comparative, randomized, controlled study of cystometry using saline and 0.3 M potassium chloride. Journal of Urology 2006;175(2):566‐570, discussion 570‐1. [21625] - PubMed
-
- Philip J, Willmott S, Owen D, Samsudin C, Irwin PP. A double‐blind, randomized controlled trial of cystometry using saline versus 0.3 M potassium chloride infusion in women with overactive bladder syndrome. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2007;26(1):110‐4. [22576] - PubMed
Radley 2001 {published data only}
-
- Radley SC, Rosario DJ, Chapple CR. Inter‐observer agreement in interpreting ambulatory urodynamics in women. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 30th Annual Meeting; 2000 Aug; Tampere, Finland. 2000:Abstract 265.
-
- Radley SC, Rosario DJ, Chapple CR, Farkas AG. Conventional and ambulatory urodynamic findings in women with symptoms suggestive of bladder overactivity. Journal of Urology 2001;166(6):2253‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Rosario DJ, Chapple CR, Radley SC. Inter‐observer agreement in interpreting ambulatory urodynamics in women. Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 30th Annual Meeting; 2002 Aug; Tampere, Finland. 2000:Abstract 359.
Realfonso 2005 {published data only}
-
- Realfonso T, Mauro U, Campitelli A, Angrisani R, Sanseverino R. Influence of the bladder filling speed over the voiding phase in the pressure flow study in the woman (Abstract number 680). Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Continence Society (ICS); 2005 Aug 28‐Sept 2; Montreal. 2005. [21088]
Rehme 2009 {published data only}
-
- Rehme C, Niedworok C, Rubben H, Stohrer M. A technically reduced urodynamic measuring method compared with a conventional urodynamic study (Abstract number 876). Proceedings of the 39th Annual Meeting of the International Continence Society (ICS), 2009 Sep 29 ‐ Oct 3, San Francisco, CA. 2009. [35362]
Robinson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Robinson D, Anders K, Cardozo L, Bidmead J, Toozs‐Hobson P, Khullar V. Can ultrasound replace ambulatory urodynamics when investigating women with irritative urinary symptoms?. BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2002;109(2):145‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rovner 2005 {published data only}
-
- Rovner E, Payne C, Yalla S, Nitti V. Response to fesoterodine in overactive bladder (OAB) patients is independent of the urodynamic finding of detrusor overactivity (Abstract number 147). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 35th Annual Meeting. 2005 Aug 28 ‐ Sep 2, Montreal, Canada, 2005.
Sand 1985 {published data only}
-
- Sand PK, Bowen LW, Ostergard DR. The effect of a filling catheter during urodynamics (Abstract). Proceedings of the American Urogynecology Society, 6th Annual Meeting; 1985 Nov 6‐9; San Diego, California. 1985.
-
- Sand PK, Bowen LW, Ostergard DR. The effect of a filling catheter during urodynamics (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Urogynecology Association, 9th Annual Meeting; 1985 Sept 9‐11; Budapest, Hungary. 1985.
Scaldazza 2005 {published data only}
-
- Scaldazza CV, Morosetti C. Effect of different sized transurethral catheters on pressure‐flow studies in women with lower urinary tract symptoms. Urologia Internationalis 2005;75(1):21‐5. [20808] - PubMed
Schmidt 2001 {published data only}
-
- Schmidt F, Jorgensen TM, Djurhuus JC. Ambulatory urodynamics and home flowmetry, are there differences in the recorded data (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 31st Annual Meeting; 2001 Sept 18‐21; Seoul, Korea. 2001:Abstract 13.
Shukla 2006 {published data only}
-
- Shukla A, Johnson D, Bibby J. Impact of patient position on filling phase of urodynamics in women. International Urogynecology Journal 2006;17(3):231‐3. [21915] - PubMed
Siracusano 2004 {published data only}
-
- Siracusano S, Knez R, Tiberio A, Alfano V, Giannantoni A, Pappagallo G. The usefulness of antibiotic prophylaxis in invasive urodynamics in postmenopausal female subjects. International Urogynecology Journal 2008;19(7):939‐42. [27793] - PubMed
-
- Siracusano S, Tiberio A, Cucchi A, Simonazzi M, Facchini M, Alfano V, et al. Usefulness of antibiotic prophylaxis in invasive urodynamics in fertile and in post menopausal female subjects (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (34th Annual Meeting) and the International UroGynecological Association; 2004 Aug 23‐27; Paris. 2004:Abstract number 753.
Sirls 2013 {published data only}
Slack 2004 {published data only}
-
- Culligan PJ, Lewis‐Priestley J, Blackwell L, Tate SB. Can urethral retroresistance pressures predict midurethral sling outcomes?. Journal of Reproductive Medicine 2010;55(3‐4):103‐7. [39947] - PubMed
-
- Slack M, Culligan P, Tracey M, Hunsicker K, Patel B, Sumeray M. Relationship of urethral retro‐resistance pressure to urodynamic measurements and incontinence severity. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2004;23(2):109‐14. [17437] - PubMed
Slack 2004a {published data only}
-
- Slack M, Hunsicker K, Patel B, Godwin A, Owens C. Comparison of multichannel cystometrogram (PVES, PABD, PDET) to single channel cystometrogram (PVES) (Abstract number 72). Progres en Urologie 2004;14(3 Suppl 3):23. [31089]
Soligo 2002 {published data only}
-
- Soligo M, Salvatore S, Arcari V, Citterio S, Malberti S, Lalia M, et al. Cough stress test and urodynamics: do they correlate? (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 32nd Annual Meeting; 2002 Aug 28‐30; Heidelberg, Germany. 2002:90‐1 (Abstract 166).
Sullivan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Sullivan J, Lewis P, Howell S, Shepherd A, Abrams P. Does contrast medium affect the results of urodynamics? (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 29th Annual Meeting; 1999 Aug; Denver, Colorado. 1999:98‐9 (Abstract 331).
Sullivan 2001 {published data only}
-
- Sullivan J, Bulmer P, Lewis P, Howell S, Shepherd A, Swithinbank L, et al. Small changes in filling medium temperature and filling rate affect urodynamic results. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2001; Vol. 20, issue 4:567‐8 (Abstract 121).
Sutherst 1984 {published data only}
Swift 1997 {published data only}
-
- Swift SE. The reliability of performing a screening cystometrogram using a fetal monitoring device for the detection of detrusor instability. Obstetrics and Gynecology 1997;89(5 Pt 1):708‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Swithinbank 1995 {published data only}
-
- Swithinbank LV, Lewis PA, Abrams P. Low detrusor compliance in neurologically normal women ‐ the need for a working definition (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 25th Annual Meeting; 1995 Oct; Sydney, Australia. 1995:426‐7 (Abstract 326).
Truzzi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Truzzi JC, Bruschini H, Srougi M. Interferences of fluid osmolality in vesical parameters during urodynamic examination (Abstract). Proceedings of the International Continence Society (ICS), 29th Annual Meeting; 1999 Aug 22‐26; Denver, Colorado. 1999:92.
Visco 2004 {published data only}
-
- Visco A. Comparison of measurements obtained with microtip and external water pressure transducers (Abstract). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2004;23(5/6):588‐9. [19019] - PubMed
Visco 2008 {published data only}
-
- Visco AG, Brubaker L, Nygaard I, Richter HE, Cundiff G, Fine P, et al. The role of preoperative urodynamic testing in stress‐continent women undergoing sacrocolpopexy: the Colpopexy and Urinary Reduction Efforts (CARE) randomized surgical trial.. International Urogynecology Journal 2008;19(5):607‐14. - PMC - PubMed
Voorham‐Van 2007 {published data only}
-
- Voorham‐Van Der Zalm PJ, Pelger RCM, Ouwerkerk TJ, Elzevier HW, Lycklama a Nijeholt GAB. Impact of intra vaginal electrostimulation on urodynamic parameters in the overactive bladder syndrome (Abstract number ?90164). Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the American Urological Association (AUA), 2007 May 19‐24, Anaheim CA. 2007. [23768]
Wadie 2009 {published data only}
-
- Wadie BS, Hefnawy AS. Urethral pressure meaurement in stress incontinence: does it help?. International Urology and Nephrology 2009;41(3):491‐5. - PubMed
Yip 2006 {published data only}
-
- Yip S, Cheon C, Wong T, Pang M, Lee L, Yuen C, et al. A randomised double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial of prophylactic antibiotics in preventing female urinary tract infection after urodynamic study (Abstract number 99). Neurourology and Urodynamics 2006;25(6):627‐8. [26628]
-
- Yip SK, Cheon C, Wong T, Pang MW, Lee L, Yuen C, et al. Preventing female urinary tract infection caused by urodynamic study: a randomised double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial of prophylactic Augmentin (Abstract number 47). International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction 2006;17 Suppl 2:S85‐6. [34184]
Zehnder 2008 {published data only}
-
- Zehnder P, Roth B, Burkhard FC, Kessler TM. Air charged and microtip catheters cannot be used interchangeably for urethral pressure measurement: a prospective, single‐blind, randomized trial. Journal of Urology 2008;180(3):1013‐7. [27508] - PubMed
Zerin 1993 {published data only}
-
- Zerin JM. Impact of contrast medium temperature on bladder capacity and cystographic diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux in children. Radiology 1993;187(1):161‐4. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Romero Maroto 2010 {published data only}
-
- Romero Maroto J, Ortiz Gorraiz MA, Gomez Perez L, Lopez Lopez A, Sanchez A, Pacheco Bru JJ. Does pressure flow study improve the outcome of surgery in women with SUI?. European Eurology Supplements 2010;9(2):228.
References to ongoing studies
Hilton 2011 {published data only}
-
- Murdoch M, McColl E, Howel D, Deverill M, Buckley BS, Lucas M, et al. INVESTIGATE‐I (INVasive Evaluation before Surgical Treatment of Incontinence Gives Added Therapeutic Effect?): study protocol for a mixed methods study to assess the feasibility of a future randomised controlled trial of the clinical utility of invasive urodynamic testing. Trials [Electronic Resource] 2011;12:169. [SR‐INCONTid41694] - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Abrams 2002
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Fall M, Griffiths D, Rosier P, Ulmsten U, et al. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub‐committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2002;21(2):167‐78. - PubMed
Abrams 2009
-
- Abrams P, Cardozo L, Khoury S, Wein A. Incontinence, 4th International Consultation on Incontinence. 4. Paris: Editions 21, 2009.
AHCPR 1996
-
- Fantl JA, Newman DK, Colling J, DeLancey JOL, Keeys C, Loughery R, et al. Chapter 2: Identifying and evaluating urinary incontinence. In: Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, editor(s). Urinary Incontinence in Adults: Acute and Chronic Management. 2. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, 1996.
Alhasso 2005
Alhasso 2006
Black 1997
Black 1998
-
- Black N. Impact of surgery for stress incontinence on morbidity. Author's reply [letter]. BMJ 1998;317(7151):144. - PubMed
Campbell 2007
Cardozo 1980
-
- Cardozo LD, Stanton SL. Genuine stress incontinence and detrusor instability‐‐a review of 200 patients. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1980;87(3):184‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chapple 2006
-
- Chapple CR, Roehrborn CG. A shifted paradigm for the further understanding, evaluation, and treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in men: Focus on the bladder. European Urology April 2006;49(4):651‐9. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Duggan 2003
-
- Duggan PM, Wilson PD, Norton P, Brown AD, Drutz HP, Herbison P. Utilization of preoperative urodynamic investigations by gynecologists who frequently operate for female urinary incontinence. International Urogynecology Journal 2003;14(4):282‐7. - PubMed
Fowler 2006
-
- Fowler G, Richmond D. Urodynamics: a mandatory preoperative investigation?. The Obstetrician and Gynaecologist 2006;8:86‐90.
Gorton 1999
-
- Gorton E, Stanton S. Women's attitudes to urodynamics: a questionnaire survey. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1999;106(8):851‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gorton 2000
-
- Gorton E, Stanton S. Ambulatory urodynamics: do they help clinical management?. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2000;107(3):316‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Griffiths 2005
-
- Griffiths D, Kondo A, Bauer S, Diamant N, Liao L, Lose G, et al. Dynamic testing. Incontinence: 3rd International Consultation on Incontinence. 3nd. Paris, France: Health Publication Ltd, 2005.
Haylen 2010
-
- Haylen BT, Ridder D, Freeman RM, Swift SE, Berghmans B, Lee J, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) Joint Report on the Terminology for Female Pelvic Floor Dysfunction. Neurourology and Urodynamics 2010;29:4‐20. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Homma 1999
-
- Homma Y, Batista JE, Bauer SB, Griffiths DJ, Hilton P, Kramer G, et al. Urodynamics. In: Abrams P, Wein A, Schussler B, Kawabi K, Bump R, Melchior H, et al. editor(s). Incontinence. First International Consultation on Incontinence. Recommendations of the International Scientific Committee: the evaluation and treatment of urinary incontinence. Plymouth,UK: Health Publication Ltd, 1999:Chapter 9.
Hosker 2009
-
- Hosker G, Rosier P, Gajewski J, Sand P. Dynamic Testing. In: Abrams P, Cardozo L, Khoury S, Wein A editor(s). Incontience: 4th International Consultation on Incontinence. Paris: Health Publication Ltd, 2009:413‐522.
Hunskaar 2002
-
- Hunskaar S, Burgio K, Diokno AC, Herzog AR, Hjalmas K, Lapitan M. Epidemiology and natural history of urinary incontinence. Incontinence: 2nd International Consultation on Incontinence. Plymouth, UK: Health Publication Ltd, 2002:165‐202.
Jarvis 1980
-
- Jarvis GJ, Hall S, Stamp S, Millar DR, Johnson A. An assessment of urodynamic examination in incontinent women. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1980;87(10):893‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Latthe 2012
Lose 1996
-
- Lose G, Thyssen H. Reproducibility of cystometry and pressure‐flow parameters in female patients. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1996;15:302‐3.
Lose 1998a
-
- Lose G, Fantl JA, Victor A, Walter S, Wells TL, Wyman J, et al. Outcome measures for research in adult women with symptoms of lower urinary tract dysfunction. Neurourology and Urodynamics 1998;17(3):255‐62. - PubMed
LUTS Guideline 2010
-
- National Clinical Guideline Centre, National Institute for Health & Clinical Excellence (NICE). The management of lower urinary tract symptoms in men. http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/12984/48554/48554.pdf 2010 (last accessed 5 December 2011).
Madhuvrata 2012
Mariappan 2005
Nabi 2006
NCCWCH 2006
-
- National Collaborating Centre for Women's & Children's Health. Urinary Incontinence ‐ the management of urinary incontinence in women. Commissioned by the National Institute for Health & Clinical Excellence. London: RCOG Press, 2006.
RCOG 2003
-
- RCOG. Guideline No. 35. Surgical management of urodynamic stress incontinence. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, UK, 2006.
Sevestre 2003
-
- Sevestre S, Ciofu C, Deval B, Traxer O, Amarenco G, Haab F. Results of the tension‐free vaginal tape technique in the elderly. European Urology 2003;44(1):128‐31. - PubMed
Sorensen 1988
-
- Sorensen S, Gregersen H, Sorensen SM. Long term reproducibility of urodynamic investigations in healthy fertile females. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology Supplementum 1988;114:35‐41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

