Immunosignatures can predict vaccine efficacy
- PMID: 24167296
- PMCID: PMC3831987
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1309390110
Immunosignatures can predict vaccine efficacy
Abstract
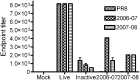
The development of new vaccines would be greatly facilitated by having effective methods to predict vaccine performance. Such methods could also be helpful in monitoring individual vaccine responses to existing vaccines. We have developed "immunosignaturing" as a simple, comprehensive, chip-based method to display the antibody diversity in an individual on peptide arrays. Here we examined whether this technology could be used to develop correlates for predicting vaccine effectiveness. By using a mouse influenza infection, we show that the immunosignaturing of a natural infection can be used to discriminate a protective from nonprotective vaccine. Further, we demonstrate that an immunosignature can determine which mice receiving the same vaccine will survive. Finally, we show that the peptides comprising the correlate signatures of protection can be used to identify possible epitopes in the influenza virus proteome that are correlates of protection.
Keywords: antibody repertoire; epitope prediction; immune profile; peptide microarray; systems vaccinology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: S.A.J. declares ownership in HealthTell, Inc, a diagnostic chip manufacturing company.
Figures




References
-
- Rerks-Ngarm S, et al. MOPH-TAVEG Investigators Vaccination with ALVAC and AIDSVAX to prevent HIV-1 infection in Thailand. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(23):2209–2220. - PubMed
-
- Plotkin SA. Vaccines: Correlates of vaccine-induced immunity. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47(3):401–409. - PubMed
-
- Plotkin SA. Complex correlates of protection after vaccination. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(10):1458–1465. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

