Systolic peak detection in acceleration photoplethysmograms measured from emergency responders in tropical conditions
- PMID: 24167546
- PMCID: PMC3805543
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076585
Systolic peak detection in acceleration photoplethysmograms measured from emergency responders in tropical conditions
Abstract
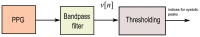
Photoplethysmogram (PPG) monitoring is not only essential for critically ill patients in hospitals or at home, but also for those undergoing exercise testing. However, processing PPG signals measured after exercise is challenging, especially if the environment is hot and humid. In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm that can detect systolic peaks under challenging conditions, as in the case of emergency responders in tropical conditions. Accurate systolic-peak detection is an important first step for the analysis of heart rate variability. Algorithms based on local maxima-minima, first-derivative, and slope sum are evaluated, and a new algorithm is introduced to improve the detection rate. With 40 healthy subjects, the new algorithm demonstrates the highest overall detection accuracy (99.84% sensitivity, 99.89% positive predictivity). Existing algorithms, such as Billauer's, Li's and Zong's, have comparable although lower accuracy. However, the proposed algorithm presents an advantage for real-time applications by avoiding human intervention in threshold determination. For best performance, we show that a combination of two event-related moving averages with an offset threshold has an advantage in detecting systolic peaks, even in heat-stressed PPG signals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
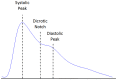

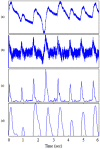
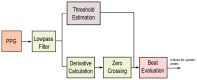

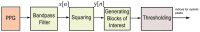
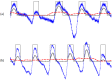
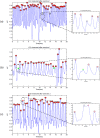
 while the dashed signal is the second moving average
while the dashed signal is the second moving average  . The squares are the blocks of interest.
. The squares are the blocks of interest.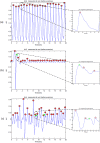
References
-
- Kimm SYS, Payne GH, Stylianou MP, Waclawiw MA, Lichtenstein C (1998) National trends in the management of cardiovascular disease risk factors in children: Second NHLBI survey of primary care physicians. Pediatrics 102: e50. - PubMed
-
- Strong J, Malcom G, McMahan C, Tracy R, Newman W, et al. (1999) Prevalence and extent of atherosclerosis in adolescents and young adults. implications for prevention from the pathobiological determinants of atherosclerosis in young study. JAMA 281: 727–737. - PubMed
-
- Leeson CPM, Whincup PH, Cook DG, Mullen MJ, Donald AE, et al. (2000) Cholesterol and arterial distensibility in the first decade of life: A population-based study. Circulation 101: 1533–1538. - PubMed
-
- Otsuka T, Kawada T, Katsumata M, Ibuki C (2006) Utility of second derivative of the finger photoplethysmogram for the estimation of the risk of coronary heart disease in the general population. Circulation Journal 70: 304–310. - PubMed
-
- Chrife R, Pigott V, Spodick D (1971) Measurement of the left ventricular ejection time by digital plethysmography. American Heart Journal 82: 222–227. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

