Targeting focal adhesion turnover in invasive breast cancer cells by the purine derivative reversine
- PMID: 24169345
- PMCID: PMC3844920
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.675
Targeting focal adhesion turnover in invasive breast cancer cells by the purine derivative reversine
Abstract
Background: The dynamics of focal adhesion (FA) turnover is a key determinant for the regulation of cancer cell migration. Here we investigated FA turnover in a panel of breast cancer models with distinct invasive properties and evaluated the impact of reversine on this turnover in relation to cancer cell invasion in in vitro and in vivo conditions.
Methods: Live imaging and immunofluorescence assays were used to investigate FA turnover in breast cancer cells. Biochemical studies were used to investigate the impact of reversine on FA signalling and turnover. In vivo activity was investigated using orthotopic breast cancer mouse models.
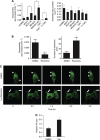
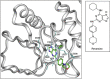
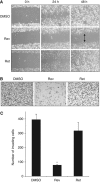
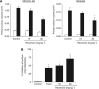
Results: Accelerated FA disassembly from plasma membrane protrusions was observed in invasive compared with non-invasive breast cancer cells or non-immortalised mammary epithelial cells. Reversine significantly inhibited FA disassembly leading to stable FAs, which was associated with reduced cell motility and invasion. The inhibitory effect of reversine on FA turnover accounted for a large part on its capacity to interfere with FAK function on regulating its downstream targets. In orthotopic breast cancer mouse models, reversine revealed a potent inhibitory activity on tumour progression to metastasis.
Conclusion: These results support the utility of targeting FA turnover as a therapeutic approach for invasive breast cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Alaoui-Jamali MA, Song DJ, Benlimame N, Yen L, Deng X, Hernandez-Perez M, Wang T. Regulation of multiple tumor microenvironment markers by overexpression of single or paired combinations of ErbB receptors. Cancer Res. 2003;63:3764–3774. - PubMed
-
- Behmoaram E, Bijian K, Jie S, Xu Y, Darnel A, Bismar TA, Alaoui-Jamali MA. Focal adhesion kinase-related proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 and focal adhesion kinase are co-overexpressed in early-stage and invasive ErbB-2-positive breast cancer and cooperate for breast cancer cell tumorigenesis and invasiveness. Am J Pathol. 2008;173:1540–1550. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

