Impact of sentinel node biopsy on long-term quality of life in breast cancer patients
- PMID: 24169352
- PMCID: PMC3844912
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2013.658
Impact of sentinel node biopsy on long-term quality of life in breast cancer patients
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to assess long-term quality of life (QoL) over a period of 6 years in women with breast cancer (BC) who underwent sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB), axillary lymph node dissection (ALND), or SLNB followed by ALND.
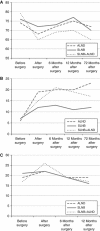
Methods: The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC-QLQ)-C30 and the EORTC-QLQ-BR-23 questionnaires were used to assess QoL before surgery, just after surgery, 6, 12 and 72 months later. The longitudinal effect of surgical modalities on QoL was assessed with a mixed model analysis of variance for repeated measurements.
Results: Five hundred and eighteen BC patients were initially included. The median follow-up was 6 years. During the follow-up, 61 patients died. None of the patients of the SLNB group developed lymphedema during follow-up and the relapse rate was similar in the different groups (P=0.62). Before surgery, global health status (P=0.52) and arm symptoms (BRAS) (P=0.99) QoL scores were similar whatever the surgical procedure. The BRAS score (P=0.0001) was better in the SLNB group 72 months after surgery. Moreover, during follow-up, patients treated with SLNB had lower arm symptoms scores than ALND patients and there was no difference for arm symptoms between patients treated with ALND and those treated with SLNB followed by complementary ALND.
Conclusion: Long-term follow-up showed that SLNB was associated with less morbidity than ALND.
Figures
References
-
- Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC, et al. The European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993;85:365–376. - PubMed
-
- Akaike Hirotugu. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Auto Control. 1974;19 (6:716–723.
-
- Burak WE, Hollenbeck ST, Zervos EE, Hock KL, Kemp LC, Young DC. Sentinel lymph node biopsy results in less postoperative morbidity compared with axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer. Am J Surg. 2002;183 (1:23–27. - PubMed
-
- Dabakuyo TS, Fraisse J, Causeret S, Gouy S, Padeano MM, Loustalot C, Cuisenier J, Sauzedde JM, Smail M, Combier JP, Chevillote P, Rosburger C, Boulet S, Arveux P, Bonnetain F. A multicenter cohort study to compare quality of life in breast cancer patients according to sentinel lymph node biopsy or axillary lymph node dissection. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:1352–1361. - PubMed
-
- Del Bianco P, Zavagno G, Burelli P, Burelli P, Scalco G, Barutta L, Carraro P, Pietrarota P, Meneghini G, Morbin T, Tacchetti G, Pecoraro P, Belardinelli V, De Salvo GL, GIVOM Morbidity comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy versus conventional axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer patients: results of the sentinella- GIVOM Italian randomised clinical trial. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34 (5:508–513. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical