Defocus Incorporated Soft Contact (DISC) lens slows myopia progression in Hong Kong Chinese schoolchildren: a 2-year randomised clinical trial
- PMID: 24169657
- PMCID: PMC3888618
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2013-303914
Defocus Incorporated Soft Contact (DISC) lens slows myopia progression in Hong Kong Chinese schoolchildren: a 2-year randomised clinical trial
Abstract
Aims: To determine if 'Defocus Incorporated Soft Contact' (DISC) lens wear slows childhood myopia progression.
Methods: A 2-year double-blind randomised controlled trial was carried out in 221 children aged 8-13 years, with myopia between -1.00 and -5.00 Dioptres (D) and astigmatism ≤1.00 D. Subjects were randomly assigned to the DISC (n=111) or single vision (SV; n=110) contact lens group. DISC lenses incorporated concentric rings, which provided an addition of +2.50 D, alternating with the normal distance correction. Refractive error (cycloplegic autorefraction) and axial length were measured at 6-month intervals. Differences between groups were analysed using unpaired t test.
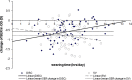
Results: In total, 128 children completed the study, n=65 in the DISC group and n=63 in the SV group. Myopia progressed 25% more slowly for children in the DISC group compared with those in the control group (0.30 D/year; 95% CI -0.71 to -0.47 vs 0.4 D/year; 95% CI -0.93 to -0.65, p=0.031). Likewise, there was less axial elongation for children in the DISC versus SV groups (0.13 mm/year; 95% CI 0.20 to 0.31 vs 0.18 mm/year; 95% CI 0.30 to 0.43, p=0.009). Treatment effect correlated positively with DISC lens wearing time (r=0.342; p=0.005). Indeed, myopia in children who wore the DISC lenses for five or more hours/day progressed 46% (mean difference=-0.382 D, p=0.001; 95% CI -0.59 to -0.17) less than those in the SV group.
Conclusions: The daily wearing of DISC lens significantly slowed myopia progression and axial elongation in Hong Kong schoolchildren. The findings demonstrated that simultaneous clear vision with constant myopic defocus can retard myopia progression.
Keywords: Child Health (Paediatrics); Clinical Trial; Contact Lens; Optics and Refraction.
Figures

References
-
- Lam CS, Edwards M, Millodot M, et al. A 2-year longitudinal study of myopia progression and optical component changes among Hong Kong schoolchildren. Optom Vis Sci 1999;76:370–80 - PubMed
-
- Lam CS, Goldschmidt E, Edwards MH. Prevalence of myopia in local and international schools in Hong Kong. Optom Vis Sci 2004;81:317–22 - PubMed
-
- Lim MC, Gazzard G, Sim EL, et al. Direct costs of myopia in Singapore. Eye 2009;23:1086–9 - PubMed
-
- Vongphanit J, Mitchell P, Wang JJ. Prevalence and progression of myopic retinopathy in an older population. Ophthalmology 2002;109:704–11 - PubMed
-
- Xu L, Wang Y, Wang S, et al. High myopia and glaucoma susceptibility the Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2007;114:216–20 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
