Nociceptin/orphanin FQ decreases glutamate transmission and blocks ethanol-induced effects in the central amygdala of naive and ethanol-dependent rats
- PMID: 24169802
- PMCID: PMC3957102
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2013.308
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ decreases glutamate transmission and blocks ethanol-induced effects in the central amygdala of naive and ethanol-dependent rats
Abstract
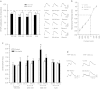
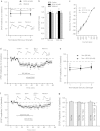
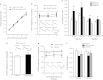
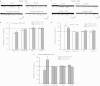
The central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) mediates several addiction-related processes and nociceptin/orphanin FQ (nociceptin) regulates ethanol intake and anxiety-like behaviors. Glutamatergic synapses, in the CeA and throughout the brain, are very sensitive to ethanol and contribute to alcohol reinforcement, tolerance, and dependence. Previously, we reported that in the rat CeA, acute and chronic ethanol exposures significantly decrease glutamate transmission by both pre- and postsynaptic actions. In this study, using electrophysiological techniques in an in vitro CeA slice preparation, we investigated the effects of nociceptin on glutamatergic transmission and its interaction with acute ethanol in naive and ethanol-dependent rats. We found that nociceptin (100-1000 nM) diminished basal-evoked compound glutamatergic receptor-mediated excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and spontaneous and miniature EPSCs (s/mEPSCs) by mainly decreasing glutamate release in the CeA of naive rats. Notably, nociceptin blocked the inhibition induced by acute ethanol (44 mM) and ethanol blocked the nociceptin-induced inhibition of evoked EPSPs in CeA neurons of naive rats. In neurons from chronic ethanol-treated (ethanol-dependent) rats, the nociceptin-induced inhibition of evoked EPSP amplitude was not significantly different from that in naive rats. Application of [Nphe1]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2, a nociceptin receptor (NOP) antagonist, revealed tonic inhibitory activity of NOP on evoked CeA glutamatergic transmission only in ethanol-dependent rats. The antagonist also blocked nociceptin-induced decreases in glutamatergic responses, but did not affect ethanol-induced decreases in evoked EPSP amplitude. Taken together, these studies implicate a potential role for the nociceptin system in regulating glutamatergic transmission and a complex interaction with ethanol at CeA glutamatergic synapses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ blockade of corticotropin-releasing factor-induced gamma-aminobutyric acid release in central amygdala is enhanced after chronic ethanol exposure.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Apr 15;71(8):666-76. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.10.032. Epub 2011 Dec 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22153590 Free PMC article.
-
CRF modulates glutamate transmission in the central amygdala of naïve and ethanol-dependent rats.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Oct;125:418-428. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.009. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28807676 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ presynaptically decreases GABAergic transmission and blocks the ethanol-induced increase of GABA release in central amygdala.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 20;103(25):9715-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601899103. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16788074 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The central amygdala and alcohol: role of γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, and neuropeptides.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012 Dec 1;2(12):a012195. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012195. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012. PMID: 23085848 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MT-7716, a novel selective nonpeptidergic NOP receptor agonist, effectively blocks ethanol-induced increase in GABAergic transmission in the rat central amygdala.Front Integr Neurosci. 2014 Feb 18;8:18. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2014.00018. eCollection 2014. Front Integr Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24600360 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of stress associated with chronic alcohol exposure on drinking.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Aug 1;122:115-126. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.04.028. Epub 2017 Apr 19. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28431971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of K+ and cation channels in ORL-1 receptor-mediated depression of neuronal excitability and epileptic activities in the medial entorhinal cortex.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Jun;151:144-158. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.04.017. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30998945 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Central Amygdala in Alcohol Dependence.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021 Feb 1;11(2):a039339. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a039339. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021. PMID: 31988201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticotropin releasing factor, but not alcohol, modulates norepinephrine release in the rat central nucleus of the amygdala.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Nov 15;179:108293. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108293. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32871155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andreasen M, Hablitz JJ. Paired-pulse facilitation in the dentate gyrus: a patch-clamp study in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:326–336. - PubMed
-
- Ciccocioppo R, Angeletti S, Panocka I, Massi M. Nociceptin/orphanin FQ and drugs of abuse. Peptides. 2000;21:1071–1080. - PubMed
-
- Ciccocioppo R, Economidou D, Fedeli A, Angeletti S, Weiss F, Heilig M, et al. Attenuation of ethanol self-administration and of conditioned reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behaviour by the antiopioid peptide nociceptin/orphanin FQ in alcohol-preferring rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2004;172:170–178. - PMC - PubMed

