Foam sclerotherapy for a symptomatic hepatic cyst: a preliminary report
- PMID: 24170168
- PMCID: PMC4024151
- DOI: 10.1007/s00270-013-0761-5
Foam sclerotherapy for a symptomatic hepatic cyst: a preliminary report
Abstract
Purpose: We evaluated our initial experience of performing sclerotherapy for symptomatic hepatic cysts using polidocanol foam instead of a liquid sclerosant.
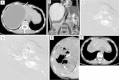
Methods: Three consecutively registered patients with symptomatic hepatic cysts (one with polycystic liver disease) underwent polidocanol foam sclerotherapy. A pigtail catheter was inserted into the targeted cyst following percutaneous cyst puncture under ultrasound guidance, and the cyst fluid was aspirated. To confirm the absence of communications between the cyst and surrounding hepatic vessels, 3 % polidocanol foam sclerosant was injected at a 1:4 ratio of polidocanol to air following digital subtraction cystography with carbon dioxide. C-arm computed tomography (CT) guidance also was used to monitor foam filling of the targeted cyst. The maximum dose of sclerosant injected per treatment session did not exceed 10 ml. The catheter was kept unclamped overnight for open drainage, and additional sclerotherapy sessions were performed on subsequent days, if needed.
Results: Efficient sclerotherapy was achieved with an average of two sessions. The initial mean cyst volume was 1,052 ml, and gradual resolution was observed without recurrence. The mean reduction rate was 97.9 % (97.7-98.3 %), and all cyst-associated symptoms disappeared. The median follow-up period was 17 (range 6-21) months. Although one patient experienced moderate-grade fever and another moderate pain at the puncture site, no major complications were observed.
Conclusion: Polidocanol foam sclerotherapy is a safe and effective treatment for symptomatic hepatic cysts.
Figures
References
-
- Kasahara A, Hayashi N, Kono M, et al. Successful treatment of a hepatic cyst by one-shot instillation of minocycline chloride. Gastroenterology. 1992;103(2):675–677. - PubMed
-
- vanSonnenberg E, Wroblicka JT, D’Agostino HB, et al. Symptomatic hepatic cysts: percutaneous drainage and sclerosis. Radiology. 1994;190(2):387–392. - PubMed
-
- Gelczer RK, Charboneau W, Hussain S, et al. Complications of percutaneous ethanol ablation. J Ultrasound Med. 1998;17(8):531–533. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

