Effect of glycemic treatment and microvascular complications on menopause in women with type 1 diabetes in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) cohort
- PMID: 24170751
- PMCID: PMC3931380
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-1746
Effect of glycemic treatment and microvascular complications on menopause in women with type 1 diabetes in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) cohort
Abstract
OBJECTIVE We examined the impact of intensive versus conventional diabetes treatment upon menopause among women with type 1 diabetes in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT), a randomized controlled trial of intensive diabetes treatment, and its observational follow-up, the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC) study. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS In a secondary analysis of women in the DCCT/EDIC (n = 657), outcomes were the cumulative incidences of natural menopause and surgical menopause. Cox regression analyses were used to examine associations with treatment group, time-varying estimates of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), insulin dosage, BMI, and microvascular complications (retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy). RESULTS By EDIC year 18, after an average of 28 years of follow-up, 240 (38%) women had experienced natural menopause and 115 (18%) women had experienced surgical menopause. Age at natural menopause was similar in the intensive versus conventional groups (49.9 vs. 49.0 years; P = 0.28), and age at surgical menopause was similar in the intensive versus conventional groups (40.8 vs. 42.0 years; P = 0.31). In multivariable models, treatment group, HbA1c, and microvascular complications were not associated with risk of natural or surgical menopause. Each 10 unit/day increase in insulin dosage decreased risk of natural menopause (hazard ratio [HR] 0.91, 95% CI 0.75-0.98) and each kg/m(2) increase in BMI increased risk of surgical menopause (HR 1.08, 95% CI 1.00-1.16). CONCLUSIONS In the DCCT/EDIC, intensive versus conventional treatment group and HbA1c level were not associated with menopause risk. Greater insulin dose was associated with lower menopause risk.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00360815 NCT00360893.
Figures
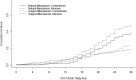
References
-
- Dorman JS, Steenkiste AR, Foley TP, et al. Familial Autoimmune and Diabetes (FAD) Study Menopause in type 1 diabetic women: is it premature? Diabetes 2001;50:1857–1862 - PubMed
-
- Bakalov VK, Anasti JN, Calis KA, et al. Autoimmune oophoritis as a mechanism of follicular dysfunction in women with 46,XX spontaneous premature ovarian failure. Fertil Steril 2005;84:958–965 - PubMed
-
- Hoek A, Schoemaker J, Drexhage HA. Premature ovarian failure and ovarian autoimmunity. Endocr Rev 1997;18:107–134 - PubMed
-
- Betterle C, Rossi A, Dalla Pria S, et al. Premature ovarian failure: autoimmunity and natural history. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1993;39:35–43 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

