Effects of Chinese Herbal Compound "Xuemai Ning"on Rabbit Atherosclerosis Model and Expression of ABCA1
- PMID: 24170990
- PMCID: PMC3809347
Effects of Chinese Herbal Compound "Xuemai Ning"on Rabbit Atherosclerosis Model and Expression of ABCA1
Abstract
Objective: To observe the lipid and the pathological changes of carotid artery smooth muscle cells in atherosclerotic rabbits, verification of Chinese herbal compound which has improve blood lipid and anti atherosclerosis effects, focus on ABCA1 as the key receptor which participated in reverse cholesterol transport, to study the mechanism of Chinese herbal compound (Xuemai Ning).
Materials and methods: 30 rabbits were randomly divided into blank group, model group and Chinese herbal compound (Xuemai Ning) group, The model group and the Xuemai Ning group with high fat diet and injection of vitamin D3, causing atherosclerosis model 4 weeks after the intervention of traditional Chinese medicine group, In the 4th week after Xuemai Ning group received the intervention of Chinese herbal compound. Blood lipid, the carotid artery pathological changes and expression of ABCA1 gene and protein in peritoneal macrophage surface were detected after 8 weeks.
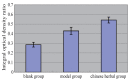
Results: The carotid artery atherosclerotic plaque formation of the model group was obvious, the carotid atherosclerotic changes of the Xuemai Ning group rabbit significantly lighter than the model group. The serum lipid of model group and Xuemai Ning group were higher than that of the blank group; and the traditional Chinese medicine can up the expression of ABCA1 protein, higher than those in the model group. Expression of macrophage ABCA1 in model group was significantly up regulated at protein level higher than the blank group; and the traditional Chinese medicine can up regulate the expression of ABCA1 protein, higher than those in the model group. Expression of ABCA1 mRNA was significantly up regulated in model group, ABCA1 mRNA of Xuemai Ning group raised more significantly.
Conclusion: Xuemai Ning can reduce triglyceride, total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein of hyperlipidemia model in rabbits serum, increase high density lipoprotein, remove foam cells in atherosclerotic cells, improve pathological of AS and up-regulate ABCA1 gene and protein so as to effectively inhibit atherosclerotic disease.
Keywords: ATP binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1); Atherosclerosis; Blood lipid; Chinese herbal medicine; Reverse Cholesterol Transport (RCT).
Figures







References
-
- Yokozawa T, Cho EJ, Sasaki S, et al. The protective role of Chinese prescription Kangen-karyu extract on diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006;29:760–765. - PubMed
-
- Liang DH. From a new target of lipid adjusting treatment about traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) lipid action mechanism and application prospects. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 2012;53(2):113–116.
-
- Chen M, Chen HX, Zhang L. Xuemai Ning treated blood dyslipidemia clinical research. Journal of Liaoning traditional Chinese medicine. 2010;37(5):803–805.
-
- Chen M, Chen HX, Su L. Effects of Chinese medicine compound on the expression of lipoprotein receptors in hyperlipidemia rat. Journal of Liaoning traditional Chinese medicine. 2010;37(2):369–371.
-
- Green TJ, Mohgadasian MH. Species-related variations in lipoprotein metabolism; the impact of FER (HDL) on susceptibility to atherogenesis. Life Sci. 2004;74(19):2441–2449. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
