A phase III, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose study of levomilnacipran extended-release in patients with major depressive disorder
- PMID: 24172209
- PMCID: PMC4047313
- DOI: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000060
A phase III, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose study of levomilnacipran extended-release in patients with major depressive disorder
Abstract
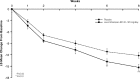
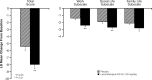
Levomilnacipran (1S, 2R-milnacipran) is a potent and selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; an extended-release (ER) formulation allows for once-daily dosing. This phase III study (NCT01034462) evaluated the efficacy, the safety, and the tolerability of 40 to 120 mg/d of levomilnacipran ER versus placebo in the treatment of patients (18-80 y) with major depressive disorder. This multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, flexible-dose study comprised a 1-week single-blind, placebo run-in period; an 8-week double-blind treatment; and a 2-week double-blind down-taper period. The primary efficacy parameter was total score change from baseline to week 8 on the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS); the secondary efficacy was the Sheehan Disability Scale. Analysis was performed using the mixed-effects model for repeated measures on a modified intent-to-treat population. A total of 434 patients received at least 1 dose of double-blind treatment (safety population); 429 patients also had 1 or more postbaseline MADRS assessments (modified intent-to-treat population). The least squares mean differences and 95% confidence interval were statistically significant in favor of levomilnacipran ER versus placebo for the MADRS total score (-3.095 [-5.256, -0.935]; P = 0.0051) and the SDS total score (-2.632 [-4.193, -1.070]; P = 0.0010) change from baseline to week 8. Adverse events were reported in 61.8% of the placebo patients and in 81.6% of the levomilnacipran ER patients. Frequently reported adverse events (≥ 5% in levomilnacipran ER and twice the rate of placebo) were nausea, dizziness, constipation, tachycardia, urinary hesitation, hyperhidrosis, insomnia, vomiting, hypertension, and ejaculation disorder. In conclusion, there was a statistically significant difference in the score change from baseline to week 8 between levomilnacipran ER and placebo on several depression rating scales, reflecting symptomatic and functional improvement; treatment was generally well tolerated.
Figures
References
-
- Israel JA. Remission in depression: definition and initial treatment approaches. J Psychopharmacol. 2006; 20 (3 suppl): 5– 10 - PubMed
-
- Hirschfeld RM, Dunner DL, Keitner G, et al. Does psychosocial functioning improve independent of depressive symptoms? A comparison of nefazodone, psychotherapy, and their combination. Biol Psychiatry. 2002; 51 (2): 123– 133 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical