Ultrasound Doppler renal resistive index: a useful tool for the management of the hypertensive patient
- PMID: 24172238
- PMCID: PMC3868026
- DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e328365b29c
Ultrasound Doppler renal resistive index: a useful tool for the management of the hypertensive patient
Abstract
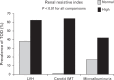
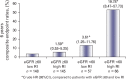
The Doppler-derived renal resistive index has been used for years in a variety of clinical settings such as the assessment of chronic renal allograft rejection, detection and management of renal artery stenosis, evaluation of progression risk in chronic kidney disease, differential diagnosis in acute and chronic obstructive renal disease, and more recently as a predictor of renal and global outcome in the critically ill patient. More recently, evidence has been accumulating showing that an increased renal resistive index not only reflects changes in intrarenal perfusion but is also related to systemic hemodynamics and the presence of subclinical atherosclerosis, and may thus provide useful prognostic information in patients with primary hypertension. On the basis of these results, the evaluation of renal resistive index has been proposed in the assessment and management of patients with primary hypertension to complement other signs of renal abnormalities.
Figures

References
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, et al. ESH-ESC Task Force on the Management of Arterial Hypertension 2007 ESH-ESC Practice Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: ESH-ESC Task Force on the Management of Arterial Hypertension. J Hypertens 2007; 25:1751–1762Erratum in: J Hypertens 2007; 25:2184 - PubMed
-
- Tublin ME, Bude RO, Platt JF. The resistive index in renal Doppler sonography: where do we stand? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003; 180:885–892 - PubMed
-
- Radermacher J, Mengel M, Ellis S, Stuht S, Hiss M, Schwarz A, et al. The renal arterial resistance index and renal allograft survival. N Engl J Med 2003; 349:115–124 - PubMed
-
- Radermacher J, Chavan A, Bleck J, Vitzthum A, Stoess B, Gebel MJ, et al. Use of Doppler ultrasonography to predict the outcome of therapy for renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med 2001; 344:410–417 - PubMed
-
- Crutchley TA, Pearce JD, Craven TE, Stafford JM, Edwards MS, Hansen KJ. Clinical utility of the resistive index in atherosclerotic renovascular disease. J Vasc Surg 2009; 49:148–155 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

