On the use of a low-cost thermal sensor to improve Kinect people detection in a mobile robot
- PMID: 24172285
- PMCID: PMC3871095
- DOI: 10.3390/s131114687
On the use of a low-cost thermal sensor to improve Kinect people detection in a mobile robot
Abstract
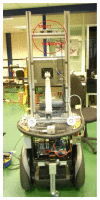
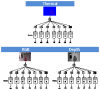
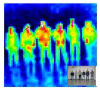
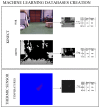
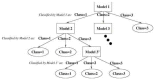
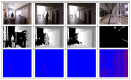
Detecting people is a key capability for robots that operate in populated environments. In this paper, we have adopted a hierarchical approach that combines classifiers created using supervised learning in order to identify whether a person is in the view-scope of the robot or not. Our approach makes use of vision, depth and thermal sensors mounted on top of a mobile platform. The set of sensors is set up combining the rich data source offered by a Kinect sensor, which provides vision and depth at low cost, and a thermopile array sensor. Experimental results carried out with a mobile platform in a manufacturing shop floor and in a science museum have shown that the false positive rate achieved using any single cue is drastically reduced. The performance of our algorithm improves other well-known approaches, such as C4 and histogram of oriented gradients (HOG).
Figures







References
-
- Shotton J., Fitzgibbon A., Cook M., Sharp T., Finocchio M., Moore R., Kipma A., Blake A. Real-Time Human Pose Recognition in Parts from a Single Depth Image. Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs; CO, USA. 20–25 June 2011.
-
- Kinect Sensor. [(accessed on 10 June 2013)]. Available online: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kinect.
-
- Heimann Sensor. [(accessed on 20 March 2013).]. Available online: http://www.heimannsensor.com/index.php.
-
- Bellotto N., Hu H. A bank of unscented Kalman filters for multimodal human perception with mobile service robots. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2010;2:121–136.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

