Differential CTLA-4 expression in human CD4+ versus CD8+ T cells is associated with increased NFAT1 and inhibition of CD4+ proliferation
- PMID: 24173147
- PMCID: PMC4284071
- DOI: 10.1038/gene.2013.57
Differential CTLA-4 expression in human CD4+ versus CD8+ T cells is associated with increased NFAT1 and inhibition of CD4+ proliferation
Abstract
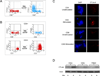
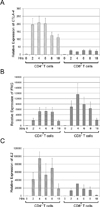
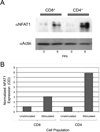
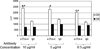
Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) is a costimulatory molecule that negatively regulates T-cell activation. Originally identified in murine CD8(+) T cells, it has been found to be rapidly induced on human T cells. Furthermore, CTLA-4 is expressed on regulatory T cells. Clinically, targeting CTLA-4 has clinical utility in the treatment of melanoma. Whether the expression of CTLA-4 is differentially regulated in CD8(+) vs CD4(+) human T cells is unclear. Here, we analyzed CTLA-4 in normal human CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell subsets and show for the first time that CTLA-4 is expressed significantly higher in the CD4(+) T cells than in CD8(+) T cells. CTLA-4 is higher at the protein and the transcriptional levels in CD4(+) T cells. This increase is due to the activation of the CTLA-4 promoter, which undergoes acetylation at the proximal promoter. Furthermore, we show that blocking CTLA-4 on CD4(+) T cells permits greater proliferation in CD4(+) vs CD8(+) cells. These findings demonstrate a differential regulation of CTLA-4 on CD4(+) and CD8(+) T-cell subsets, which is likely important to the clinical efficacy for anti-CTLA-4 therapies. The findings hint to strategies to modulate CTLA-4 expression by targeting epigenetic transcription to alter the immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any competing financial interests to declare in relation to the work described in this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Dariavach P, Mattéi M-G, Golstein P, Lefranc M-P. Human Ig superfamily CTLA-4 gene: chromosomal localization and identity of protein sequence between murine and human CTLA-4 cytoplasmic domains. European Journal of Immunology. 1988;18(12):1901–1905. - PubMed
-
- Harper K, Balzano C, Rouvier E, Mattei M, Luciani M, Golstein P. CTLA-4 and CD28 activated lymphocyte molecules are closely related in both mouse and human as to sequence, message expression, gene structure, and chromosomal location. The Journal of Immunology. 1991;147(3):1037–1044. - PubMed
-
- Lindsten T, Lee K, Harris E, Petryniak B, Craighead N, Reynolds P, et al. Characterization of CTLA-4 structure and expression on human T cells. The Journal of Immunology. 1993;151(7):3489–3499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

