The Drosophila ubiquitin-specific protease Puffyeye regulates dMyc-mediated growth
- PMID: 24173801
- PMCID: PMC3833434
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.096941
The Drosophila ubiquitin-specific protease Puffyeye regulates dMyc-mediated growth
Abstract
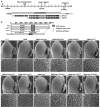
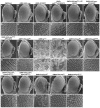
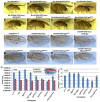
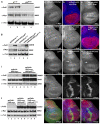
The essential and highly conserved role of Myc in organismal growth and development is dependent on the control of Myc protein abundance. It is now well established that Myc levels are in part regulated by ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation. Using a genetic screen for modifiers of Drosophila Myc (dMyc)-induced growth, we identified and characterized a ubiquitin-specific protease (USP), Puffyeye (Puf), as a novel regulator of dMyc levels and function in vivo. We show that puf genetically and physically interacts with dMyc and the ubiquitin ligase archipelago (ago) to modulate a dMyc-dependent cell growth phenotype, and that varying Puf levels in both the eye and wing phenocopies the effects of altered dMyc abundance. Puf containing point mutations within its USP enzymatic domain failed to alter dMyc levels and displayed no detectable phenotype, indicating the importance of deubiquitylating activity for Puf function. We find that dMyc induces Ago, indicating that dMyc triggers a negative-feedback pathway that is modulated by Puf. In addition to its effects on dMyc, Puf regulates both Ago and its cell cycle substrate Cyclin E. Therefore, Puf influences cell growth by controlling the stability of key regulatory proteins.
Keywords: Deubiquitinase; Drosophila; Growth; Myc; Protein degradation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Drosophila F box protein archipelago regulates dMyc protein levels in vivo.Curr Biol. 2004 Jun 8;14(11):965-74. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.04.040. Curr Biol. 2004. PMID: 15182669
-
Identification of domains responsible for ubiquitin-dependent degradation of dMyc by glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and casein kinase 1 kinases.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Jun;29(12):3424-34. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01535-08. Epub 2009 Apr 13. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19364825 Free PMC article.
-
Notch-dependent expression of the archipelago ubiquitin ligase subunit in the Drosophila eye.Development. 2011 Jan;138(2):251-60. doi: 10.1242/dev.054429. Epub 2010 Dec 9. Development. 2011. PMID: 21148181 Free PMC article.
-
Myc in stem cell behaviour: insights from Drosophila.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;786:269-85. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-6621-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23696362 Review.
-
Myc--what we have learned from flies.Curr Drug Targets. 2009 Jul;10(7):590-601. doi: 10.2174/138945009788680400. Curr Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19601763 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying USPs regulating immune signals in Drosophila: USP2 deubiquitinates Imd and promotes its degradation by interacting with the proteasome.Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Jul 16;12:41. doi: 10.1186/s12964-014-0041-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 25027767 Free PMC article.
-
A New Mode of Mitotic Surveillance.Trends Cell Biol. 2017 May;27(5):314-321. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Trends Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28188027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myc suppresses male-male courtship in Drosophila.EMBO J. 2022 Apr 4;41(7):e109905. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021109905. Epub 2022 Feb 15. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 35167135 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct gene-selective roles for a network of core promoter factors in Drosophila neural stem cell identity.Biol Open. 2019 Apr 4;8(4):bio042168. doi: 10.1242/bio.042168. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 30948355 Free PMC article.
-
A Nucleolar Isoform of the Drosophila Ubiquitin Specific Protease dUSP36 Regulates MYC-Dependent Cell Growth.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 19;8:506. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00506. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32637412 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhat K. P., Greer S. F. (2011). Proteolytic and non-proteolytic roles of ubiquitin and the ubiquitin proteasome system in transcriptional regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1809, 150–155 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

