Growth differentiation factor 5 is a key physiological regulator of dendrite growth during development
- PMID: 24173804
- PMCID: PMC3833432
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.101378
Growth differentiation factor 5 is a key physiological regulator of dendrite growth during development
Abstract
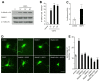
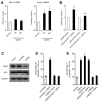
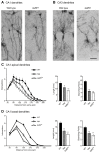
Dendrite size and morphology are key determinants of the functional properties of neurons. Here, we show that growth differentiation factor 5 (GDF5), a member of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) subclass of the transforming growth factor β superfamily with a well-characterised role in limb morphogenesis, is a key regulator of the growth and elaboration of pyramidal cell dendrites in the developing hippocampus. Pyramidal cells co-express GDF5 and its preferred receptors, BMP receptor 1B and BMP receptor 2, during development. In culture, GDF5 substantially increased dendrite, but not axon, elongation from these neurons by a mechanism that depends on activation of SMADs 1/5/8 and upregulation of the transcription factor HES5. In vivo, the apical and basal dendritic arbours of pyramidal cells throughout the hippocampus were markedly stunted in both homozygous and heterozygous Gdf5 null mutants, indicating that dendrite size and complexity are exquisitely sensitive to the level of endogenous GDF5 synthesis.
Keywords: Bone morphogenetic protein; Dendrite; Growth differentiation factor 5; Hippocampus; Mouse.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutant GDF5 enhances ameloblast differentiation via accelerated BMP2-induced Smad1/5/8 phosphorylation.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 31;6:23670. doi: 10.1038/srep23670. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27030100 Free PMC article.
-
Endoglin is involved in BMP-2-induced osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells through a pathway independent of Smad-1/5/8 phosphorylation.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Feb;222(2):465-73. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21968. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19918795
-
BMP-6 inhibits growth of mature human B cells; induction of Smad phosphorylation and upregulation of Id1.BMC Immunol. 2005 May 9;6:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-6-9. BMC Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15877825 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
BMP-Smad 1/5/8 signalling in the development of the nervous system.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Oct;109:28-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23891815 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of miR-181a promotes midbrain neuronal growth through a Smad1/5-dependent mechanism: implications for Parkinson's disease.Neuronal Signal. 2018 Jan 26;2(1):NS20170181. doi: 10.1042/NS20170181. eCollection 2018 Mar. Neuronal Signal. 2018. PMID: 32714583 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural basis of extreme conservation in vertebrate 5' untranslated regions.Nat Genet. 2021 May;53(5):729-741. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00830-1. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Nat Genet. 2021. PMID: 33821006 Free PMC article.
-
The Wnt Signaling Pathway Is Differentially Expressed during the Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Latency-Reactivation Cycle: Evidence That Two Protein Kinases Associated with Neuronal Survival, Akt3 and BMPR2, Are Expressed at Higher Levels during Latency.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e01937-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01937-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29321317 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Differentiation Factor 5 Improves Neurogenesis and Functional Recovery in Adult Mouse Hippocampus Following Traumatic Brain Injury.Front Neurol. 2018 Jul 23;9:592. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00592. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30083129 Free PMC article.
-
Region-specific role of growth differentiation factor-5 in the establishment of sympathetic innervation.Neural Dev. 2016 Feb 15;11:4. doi: 10.1186/s13064-016-0060-3. Neural Dev. 2016. PMID: 26878848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn K., Mishina Y., Hanks M. C., Behringer R. R., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd (2001). BMPR-IA signaling is required for the formation of the apical ectodermal ridge and dorsal-ventral patterning of the limb. Development 128, 4449–4461 - PubMed
-
- Andl T., Ahn K., Kairo A., Chu E. Y., Wine-Lee L., Reddy S. T., Croft N. J., Cebra-Thomas J. A., Metzger D., Chambon P., et al. (2004). Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development 131, 2257–2268 - PubMed
-
- Bragdon B., Moseychuk O., Saldanha S., King D., Julian J., Nohe A. (2011). Bone morphogenetic proteins: a critical review. Cell. Signal. 23, 609–620 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

