Concept of atherosclerosis velocity: is it a better measure of cardiovascular risk?
- PMID: 24174691
- PMCID: PMC3808944
Concept of atherosclerosis velocity: is it a better measure of cardiovascular risk?
Abstract
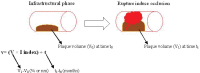
In most cases atherosclerosis is the underlying cause of vascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke. It is believed that endothelial injury is the earliest change in the artery wall and that this precedes the formation of lesions of atherosclerosis. Recent developments in the field of atherosclerosis have led to a renewed interest in the recognition of the parameter of time in the atherosclerosis process. We believe that the factors determining the time-dependent rate of atherosclerosis progression are important, and it is in this context that we wish to propose for the first time the term "atherosclerosis velocity". In this review article, we summarize the existing evidence regarding atherosclerosis velocity and discuss the importance of this issue.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Plaque; Risk factors; Velocity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lower blood flow velocity, higher resistance index, and larger diameter of extracranial carotid arteries are associated with ischemic stroke independently of carotid atherosclerosis and cardiovascular risk factors.J Clin Ultrasound. 2007 Jul-Aug;35(6):322-30. doi: 10.1002/jcu.20351. J Clin Ultrasound. 2007. PMID: 17471583
-
Local arterial stiffening assessed by MRI precedes atherosclerotic plaque formation.Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Nov;6(6):916-23. doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.113.000611. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 24100044
-
The Role of SGLT2 Inhibitors in Atherosclerosis: A Narrative Mini-Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 5;12:751214. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.751214. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34803693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient--Part III: Executive summary of the Screening for Heart Attack Prevention and Education (SHAPE) Task Force report.Am J Cardiol. 2006 Jul 17;98(2A):2H-15H. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.03.002. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Am J Cardiol. 2006. PMID: 16843744 Review.
-
Vasa Vasorum Angiogenesis: Key Player in the Initiation and Progression of Atherosclerosis and Potential Target for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 17;9:706. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00706. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29719532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A 2D FSI mathematical model of blood flow to analyze the hyper-viscous effects in atherosclerotic COVID patients.Results Eng. 2021 Dec;12:100275. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2021.100275. Epub 2021 Aug 24. Results Eng. 2021. PMID: 35317220 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in mesenchymal stem cells.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 30;13:970699. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.970699. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36110206 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Poole-Wilson PA. Global differences in atherosclerosis. In: Willerson JT, Cohn JN, editors. Cardiovascular Medicine. London: Springer-Verlag; 2007. pp. 653–8.
-
- Azarpazhooh MR, Etemadi MM, Donnan GA, Mokhber N, Majdi MR, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, et al. Excessive incidence of stroke in Iran: evidence from the Mashhad Stroke Incidence Study (MSIS), a population-based study of stroke in the Middle East. Stroke. 2010;41:e3–e10. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.559708. PubMed PMID: 19926844. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Okamoto Y, Rocha VZ, Folco E. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: transition from theory to practice. Circ J. 2010;74:213–20. PubMed PMID: 20065609. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
