Evaluation of the adequacy of general anesthesia in cesarean section by bispectral index
- PMID: 24174695
- PMCID: PMC3808948
Evaluation of the adequacy of general anesthesia in cesarean section by bispectral index
Abstract
Background: Awareness and recall, though not common, are the major hazards of general anesthesia, especially in Cesarean section (C/S) because of the absence of benzodiazepine and opioids for a significant time during anesthesia. In this study, the Bispectral Index (BIS), end-tidal isoflurane, and hemodynamic parameters were examined to evaluate the depth of the routine general anesthetic technique in C/S.
Methods: This study was carried out on 60 parturient patients undergoing elective C/S. A standardized anesthetic technique was applied: induction with Thiopental (4-5 mg/kg) and Succinylcholine (1.5-2 mg/kg) as well as maintenance with O2, N2O, and isoflurane. Electrocardiogram, heart rate, blood pressure, Spo2, end-tidal isoflurane concentration, BIS, and any clinical signs of inadequate depth of anesthesia such as movement, sweating, lacrimation, coughing, and jerking were continuously monitored and recorded at 16 fixed time points during anesthesia.
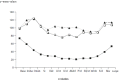
Results: A median BIS of less than 70 (range: 42-68) was obtained on all occasions during surgery; however, at each milestone, at least 20% of the patients had BIS values above 60. Hemodynamic parameters increased significantly in some patients, especially during laryngoscopy and intubation. No patient experienced recall or awareness.
Conclusion: The currently used general anesthetic technique in our center appears inadequate in some milestones to reliably produce BIS values less than 60, which are associated with lower risk of awareness. Therefore, with respect to such desirable outcomes as good Apgar and clinical status in neonates, we would recommend the application of this method (if confirmed by further studies) through larger dosages of anesthetic agents.
Keywords: Awareness; Bispectral index; Cesarean section; Recall.
Figures

References
-
- Shahbazi Sh, Zand F, Saem J. Comparative evaluation of the Cerebral state indexTM and Bispectral indexTM monitoring during propofol-remifentanil anesthesia for open heart surgery. Pak J Med Sci. 2007;23:505–9.
-
- Grover VK, Bharti N. Measuring Depth of Anaesthesia - An Overview on the Currently Available Monitoring Systems. Indian Anaesthetists' Forum. 2008;9:1–32.
-
- Yeo SN, Lo WK. Bispectral index in assessment of adequacy of general anaesthesia for lower segment caesarean section. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2002;30:36–40. PubMed PMID: 11939437. - PubMed
-
- Chin KJ, Yeo SW. A BIS-guided study of sevoflurane requirements for adequate depth of anaesthesia in Caesarean section. Anaesthesia. 2004;59:1064–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.2004.03944.x. PubMed PMID: 15479312. - PubMed
-
- Kalkman CJ, Drummond JC. Monitors of depth of anesthesia, quo vadis? Anesthesiology. 2002;96:784–7. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200204000-00003. PubMed PMID: 11964583. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
