Inhibitory effect of a mixture containing vitamin C, lysine, proline, epigallocatechin gallate, zinc and alpha-1-antitrypsin on lung carcinogenesis induced by benzo(a) pyrene in mice
- PMID: 24174951
- PMCID: PMC3810580
Inhibitory effect of a mixture containing vitamin C, lysine, proline, epigallocatechin gallate, zinc and alpha-1-antitrypsin on lung carcinogenesis induced by benzo(a) pyrene in mice
Abstract
Background: This study was aimed to evaluate protective and therapeutic effects of a specific mixture, containing vitamin C, lysine, proline, epigallocatechin gallate and zinc, as well as alpha-1-antitrypsin protein on lung tumorigenesis induced by benzo(a) pyrene [B(a)P] in mice.
Materials and methods: Swiss albino mice were divided into two main experiments, experiment (1) the mice were injected with 100 mg/kg B(a)P and lasted for 28 weeks, while experiment (2) the mice were injected with 8 doses each of 50 mg/kg B(a)P and lasted for 16 weeks. Each experiment (1 and 2) divided into five groups, group (I) received vehicle, group (II) received the protector mixture, group (III) received the carcinogen B(a)P, group (IV) received the protector together with the carcinogen (simultaneously) and group (V) received the carcinogen then the protector (consecutively).
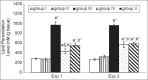
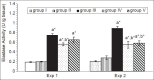
Results: Total sialic acid, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, vascular epithelial growth factor, hydroxyproline levels, as well as elastase and gelatinase activities showed significant elevation in group (III) in the two experiments comparing to control group (P < 0.001). These biochemical alterations were associated with histopathological changes. Administration of the protector in group IV and group V causes significant decrease in such parameters with improvement in histopathological alterations with improvement in histopathological alterations when compared with group III in the two experiments (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The present protector mixture has the ability to suppress neoplastic alteration and restore the biochemical and histopathological parameters towards normal on lung carcinogenesis induced by benzo(a) pyrene in mice. Furthermore, the present mixture have more protective rather than therapeutic action.
Keywords: Alpha-1-antitrypsin; benzo(a) pyrene; epigallocatechin gallate; lung tumorigenesis; lysine; proline; protector; vitamin C; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cytoprotective effect of mangiferin on benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in swiss albino mice.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008 Aug;103(2):137-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2008.00254.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18816296
-
Protective effect of piperine on benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung carcinogenesis in Swiss albino mice.Clin Chim Acta. 2004 Dec;350(1-2):73-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cccn.2004.07.004. Clin Chim Acta. 2004. PMID: 15530462
-
Modulatory effects of catechin hydrate on benzo[a]pyrene-induced nephrotoxicity in adult male albino rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 May 17;10(3):542-550. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfab029. eCollection 2021 May. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34141168 Free PMC article.
-
Indole-3-carbinol inhibits 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone plus benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice and modulates carcinogen-induced alterations in protein levels.Cancer Res. 2007 Jul 1;67(13):6502-11. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4438. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17616712
-
Antitumor activity of Cuphea ignea extract against benzo(a)pyrene-induced lung tumorigenesis in Swiss Albino mice.Toxicol Rep. 2019 Oct 11;6:1071-1085. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2019.10.004. eCollection 2019. Toxicol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31660294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Osann KE, Lowery JT, Schell MJ. Small cell lung cancer in women: Risk associated with smoking, prior respiratory disease, and occupation. Lung Cancer. 2000;28:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Hecht SS, Upadhyaya P, Wang M, Bliss RL, McIntee EJ, Kenney PM. Inhibition of lung tumorigenesis in A/J mice by N-acetyl-S-(N-2-phenethylthiocarbamoyl)-L-cysteine and myo-inositol, individually and in combination. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23:1455–61. - PubMed
-
- El-Attar I. Lung cancer in Egypt and neighboring Arab countries: Magnitude of the problem. UICC. 2005. Available from: http://www.nci.edu.eg .
-
- Travis WD, Travis LB, Devesa SS. Lung cancer. Cancer. 1995;75:191–202. - PubMed
-
- Miller YE. Lung cancer and other pulmonary neoplasms. In: Goldman L, Ausiello D, editors. Cecil Textbook of Medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2004. pp. 1201–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
