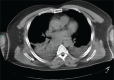
Severe gastrointestinal burn with hydrochloric acid
- PMID: 24174955
- PMCID: PMC3810584
Severe gastrointestinal burn with hydrochloric acid
Abstract
Inadvertantly or purposely, an oral intake of corrosive substances may cause life-threatening problems. Early admission to the hospital, clinical and endoscopic evaluation, and early surgery when required, may reduce morbidity and mortality. We report the case of a 49-year-old male patient, who had attempted suicide, by drinking about 800 mL of 25% hydrochloric acid, and who had severe intra-abdominal damage. The aim of this report is to state the fact that a good outcome is possible in severe burns caused by oral intake of corrosive substances, when fast, multidisciplinary, and appropriate management is provided on time.
Keywords: Corrosive ingestion; hydrochloric acid; intensive care unit.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gastrointestinal mucosal damages caused by ingestion of corrosive substances: A case study of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide.Narra J. 2023 Dec;3(3):e259. doi: 10.52225/narra.v3i3.259. Epub 2023 Dec 25. Narra J. 2023. PMID: 38450338 Free PMC article.
-
Clinico-epidemiological Characteristics of Corrosive Ingestion: A Cross-sectional Study at a Tertiary Care Hospital of Multan, South-Punjab Pakistan.Cureus. 2018 May 29;10(5):e2704. doi: 10.7759/cureus.2704. Cureus. 2018. PMID: 30062078 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal myocardial infarction after hydrochloric acid ingestion in a suicide attempt.Am J Emerg Med. 2008 Jun;26(5):634.e5-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2007.10.009. Am J Emerg Med. 2008. PMID: 18534312
-
Corrosive substances ingestion: a review.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019 Sep;49(8):637-669. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2019.1707773. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 32009535 Review.
-
Hydrogen peroxide poisoning.Toxicol Rev. 2004;23(1):51-7. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200423010-00006. Toxicol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15298493 Review.
Cited by
-
Case report of tracheobronchial injuries after acid ingestion: CT findings with serial follow-up: Airway complication after acid ingestion.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 11;99(50):e23586. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023586. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33327320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kay M, Wyllie R. Caustic ingestions in children. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2009;21:651–4. - PubMed
-
- Dogan Y, Erkan T, Cokugras FC, Kutlu T. Caustic gastroesophageal lesions in childhood: An analysis of 473 cases. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 2006;45:435–8. - PubMed
-
- Robustelli U, Bellotti R, Scardi F, Fortunato Armellino M, De Masi A, Forner AL, et al. Management of corrosive injuries of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Our experience in 58 patients. G Chir. 2011;32:188–93. - PubMed
-
- Cabral C, Chirica M, de Chaisemartin C, Gornet JM, Munoz-Bongrand N, Halimi B, et al. Caustic injuries of the upper digestive tract: A population observational study. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:214–21. - PubMed
-
- Franke DD, Davis EG, Woods DR, Johnson RK, Miller FB, Franklin GA, et al. Catastrophic gastrointestinal injury due to battery acid ingestion. J Emerg Med. 2011;40:276–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources