The Aqueous Extract of Rhizome of Gastrodia elata Protected Drosophila and PC12 Cells against Beta-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity
- PMID: 24174977
- PMCID: PMC3794658
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/516741
The Aqueous Extract of Rhizome of Gastrodia elata Protected Drosophila and PC12 Cells against Beta-Amyloid-Induced Neurotoxicity
Abstract
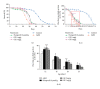
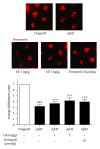
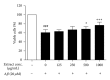
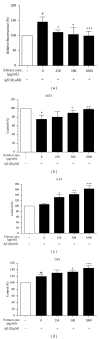
This study aims to investigate the neuroprotective effect of the rhizome of Gastrodia elata (GE) aqueous extract on beta-amyloid(A β )-induced toxicity in vivo and in vitro. Transgenic Drosophila mutants with A β -induced neurodegeneration in pan-neuron and ommatidia were used to determine the efficacy of GE. The antiapoptotic and antioxidative mechanisms of GE were also studied in A β -treated pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. In vivo studies demonstrated that GE (5 mg/g Drosophila media)-treated Drosophila possessed a longer lifespan, better locomotor function, and less-degenerated ommatidia when compared with the A β -expressing control (all P < 0.05). In vitro studies illustrated that GE increased the cell viability of A β -treated PC12 cells in dose-dependent manner, probably through attenuation of A β -induced oxidative and apoptotic stress. GE also significantly upregulated the enzymatic activities of catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase, leading to the decrease of reactive oxidation species production and apoptotic marker caspase-3 activity. In conclusion, our current data presented the first evidence that the aqueous extract of GE was capable of reducing the A β -induced neurodegeneration in Drosophila, possibly through inhibition of apoptosis and reduction of oxidative stress. GE aqueous extract could be developed as a promising herbal agent for neuroprotection and novel adjuvant therapies for Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolonged oral administration of Gastrodia elata extract improves spatial learning and memory of scopolamine-treated rats.Lab Anim Res. 2015 Jun;31(2):69-77. doi: 10.5625/lar.2015.31.2.69. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Lab Anim Res. 2015. PMID: 26155201 Free PMC article.
-
The aqueous extract of rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume attenuates locomotor defect and inflammation after traumatic brain injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Jun 5;185:87-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.03.018. Epub 2016 Mar 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26979339
-
Gastrodia and Uncaria (tianma gouteng) water extract exerts antioxidative and antiapoptotic effects against cerebral ischemia in vitro and in vivo.Chin Med. 2016 May 31;11:27. doi: 10.1186/s13020-016-0097-6. eCollection 2016. Chin Med. 2016. PMID: 27252774 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropharmacological effects of Gastrodia elata Blume and its active ingredients.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1574277. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1574277. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40371076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume - An ethnopharmacological review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Aug 2;189:361-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.06.057. Epub 2016 Jul 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27377337 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of traditional medicines for neurodegenerative diseases using Drosophila models.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:967462. doi: 10.1155/2014/967462. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24790636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropharmacological Potential of Gastrodia elata Blume and Its Components.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:309261. doi: 10.1155/2015/309261. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26543487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol derivatives and their sedative-hypnotic activities.RSC Adv. 2018 May 29;8(35):19539-19550. doi: 10.1039/c8ra01972j. eCollection 2018 May 25. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540981 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged oral administration of Gastrodia elata extract improves spatial learning and memory of scopolamine-treated rats.Lab Anim Res. 2015 Jun;31(2):69-77. doi: 10.5625/lar.2015.31.2.69. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Lab Anim Res. 2015. PMID: 26155201 Free PMC article.
-
N-Butanol Extract of Gastrodia elata Suppresses Inflammatory Responses in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages and Complete Freund's Adjuvant- (CFA-) Induced Arthritis Rats via Inhibition of MAPK Signaling Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jan 21;2020:1658618. doi: 10.1155/2020/1658618. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32063980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schnabel J. Amyloid: little proteins, big clues. Nature. 2011;475(7355):S12–S14. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297(5580):353–356. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer's Disease International. World Alzheimer Report. London, UK: Alzheimer's Disease International;
-
- Gravitz L. Drugs: a tangled web of targets. Nature. 2011;475(7355):S9–S11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

