Gene expression profiling on the molecular action of danshen-gegen formula in a randomized placebo-controlled trial of postmenopausal women with hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 24174980
- PMCID: PMC3794622
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/703705
Gene expression profiling on the molecular action of danshen-gegen formula in a randomized placebo-controlled trial of postmenopausal women with hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
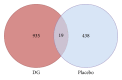
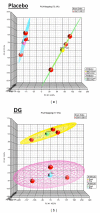
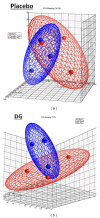
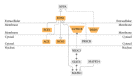
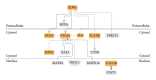
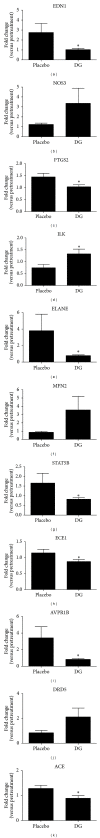
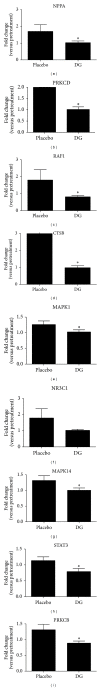
The Danshen-Gegen formula (DG) is a traditional Chinese herbal formula which has long been used to treat cardiovascular disease. DG was found to be a cardiovascular tonic in our recent research. However, a comprehensive investigation of the molecular mechanism of DG in cardiovascular disease has not been performed. The aim of this study was to clarify the transcriptional profiling of genes modulated by DG on postmenopausal women by using DNAmicroarray technology. We obtained 29 whole blood samples both from DG-treated and placebo-treated subjects. Blood lipid profile and intima-media thickness (IMT) were measured. Affymetrix GeneChip was used to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs), followed by validation by the real-time PCR method. The results showed that DG-treated group has a significant improvement in IMT and lipid profile as compared to placebo-treated group. For the genomic study, the DG-treated group has a higher number of DEGs identified as compared to the placebo-treated group. Two important biological processes of "regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by hormone" and "regulation of smooth muscle proliferation" have been identified by GePS in the DG-treated group. No significant biological process and cellular components were identified in the placebo-treated group. This genomic study on the molecular action of DG in postmenopausal women gathered sufficient molecular targets and pathways to reveal that DG could improve neointima thickening and hypertension.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A randomized placebo controlled trial of an innovative herbal formula in the prevention of atherosclerosis in postmenopausal women with borderline hypercholesterolemia.Complement Ther Med. 2014 Jun;22(3):473-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2014.03.010. Epub 2014 Apr 6. Complement Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24906587 Clinical Trial.
-
Danshen-Gegen decoction exerts proliferative effect on rat cardiac myoblasts H9c2 via MAPK and insulin pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Oct 31;138(1):60-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.027. Epub 2011 Sep 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21907783
-
The anti-hypertensive effect of Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) and Gegen (Pueraria lobata) formula in rats and its underlying mechanisms of vasorelaxation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Oct 11;137(3):1366-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.08.006. Epub 2011 Aug 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21855622
-
A herbal formula containing roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) and Pueraria lobata (Gegen) inhibits inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through inhibition of nuclear factor κB (NFκB) pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Feb 13;145(3):776-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.011. Epub 2012 Dec 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23261483
-
Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine for patients with postmenopausal hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Mar;141:481-500. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.01.018. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30639372
Cited by
-
Supplementation with the Traditional Thai Polyherbal Medicine NawaTab Ameliorates Lipid Profiles in High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemic Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Nov 21;2022:8574756. doi: 10.1155/2022/8574756. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36452138 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the traditional Chinese medicinal herbs and formulae with hypolipidemic effect.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:925302. doi: 10.1155/2014/925302. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25110708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal Plants as a Potential and Successful Treatment Option in the Context of Atherosclerosis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 8;11:403. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00403. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32322201 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rosano GMC, Vitale C, Marazzi G, Volterrani M. Menopause and cardiovascular disease: the evidence. Climacteric. 2007;10(supplement 1):19–24. - PubMed
-
- Rozenberg S, Vandromme J, Antoine C. Postmenopausal hormone therapy: risks and benefits. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2013;9(4):216–227. - PubMed
-
- Cheung DW, Koon CM, Wat E, et al. A herbal formula containing roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) and Pueraria lobata (Gegen) inhibits inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through inhibition of nuclear factor κB (NF κB) pathway. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2013;145(3):776–783. - PubMed
-
- Deng Y, Ng ESK, Yeung JHK, et al. Mechanisms of the cerebral vasodilator actions of isoflavonoids of Gegen on rat isolated basilar artery. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2012;139(1):294–304. - PubMed
-
- Lam FFY, Deng SY, Ng ESK, et al. Mechanisms of the relaxant effect of a Danshen and Gegen formulation on rat isolated cerebral basilar artery. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2010;132(1):186–192. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

