Epimedium flavonoids counteract the side effects of glucocorticoids on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
- PMID: 24174984
- PMCID: PMC3794657
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/938425
Epimedium flavonoids counteract the side effects of glucocorticoids on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
Abstract
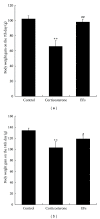
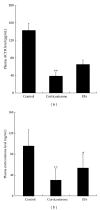
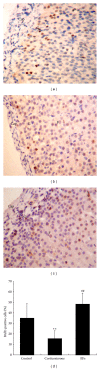
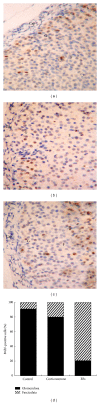
Our previous studies demonstrated that the epimedium herb, when simultaneously used with GCs, counteracted suppressive effects of GCs on the HPA axis without adverse influence on the therapeutic action of GCs. Here, total flavones were extracted from the epimedium flavonoids (EFs) and then used to investigate whether EFs provide protective effects on the HPA axis. We found that GCs induced a significant decrease in body weight gain, adrenal gland weight gain, and plasma adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) and corticosterone levels. After treatment with EFs, body weight gain, adrenal gland weight gain, and plasma corticosterone level were significantly restored, whilst plasma ACTH level was partially elevated. EFs were also shown to promote cell proliferation in the outer layer of adrenal cortex and to enhance the migration of newly divided cells toward the inner layer. To elucidate the underlying mechanisms, the mRNA expression of insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II) was measured, and EFs significantly upregulated IGF-II expression. Our results indicated that EFs counteract the suppression of the HPA axis induced by GCs. This may involve both the ACTH and IGF-II pathways and thereby promote regeneration of the adrenal cortex suggesting a potential clinical application of EFs against the suppressive effects of GCs on the HPA axis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concomitant infusion of ovine corticotropin-releasing hormone does not prevent suppression of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis by dexamethasone in male rats.J Endocrinol Invest. 1997 Jul-Aug;20(7):393-6. doi: 10.1007/BF03347990. J Endocrinol Invest. 1997. PMID: 9309537
-
Experimentally-induced hyperthyroidism is associated with activation of the rat hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis.Eur J Endocrinol. 2005 Jul;153(1):177-85. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.01923. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15994759
-
[Exploration on molecular mechanism of Epimediun flavonoids in regulating adrenocortical regeneration in rats with inhibited hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis using oligonucleotide microarrays].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2006 May;26(5):423-6. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16883909 Chinese.
-
Extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis: immune regulation and aspects on local organ homeostasis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Nov 5;380(1-2):89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.05.007. Epub 2013 May 21. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23707789 Review.
-
Diabetes and the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.Minerva Endocrinol. 2003 Jun;28(2):87-102. Minerva Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12717340 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic and physiological analysis of the response of Spirodela polyrrhiza to sodium nitroprusside.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Feb 8;24(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04766-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38331719 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal plants' proposed nanocomposites for the management of endocrine disorders.Heliyon. 2022 Sep 18;8(9):e10665. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10665. eCollection 2022 Sep. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36185142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combining Traditional Chinese Herbs and csDMARDs for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Involves Tapering and Discontinuing Glucocorticoids: Protocol for a Two-Stage Non-Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Mar 5;17:827-839. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S444056. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38481616 Free PMC article.
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Invigorating Kidney and Supplementing Qi Chinese Herbal Formulae in Asthma Patients.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:3754145. doi: 10.1155/2017/3754145. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28740537 Free PMC article.
-
High flavonoid accompanied with high starch accumulation triggered by nutrient starvation in bioenergy crop duckweed (Landoltia punctata).BMC Genomics. 2017 Feb 15;18(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3559-z. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28201992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hughes RA, Mehndiratta MM. Corticosteroids for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2002;(8)CD002062 - PubMed
-
- Suzuki K. Current therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma. Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2013;43(2):116–124. - PubMed
-
- Vayssière BM, Dupont S, Choquart A, et al. Synthetic glucocorticoids that dissociate transactivation and AP-1 transrepression exhibit antiinflammatory activity in vivo. Molecular Endocrinology. 1997;11(9):1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Resche-Rigon M, Gronemeyer H. Therapeutic potential of selective modulators of nuclear receptor action. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 1998;2(4):501–507. - PubMed
-
- Hopkins RL, Leinung MC. Exogenous Cushing’s syndrome and glucocorticoid withdrawal. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America. 2005;34(2):371–384. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

