The Protective Effect of Cordymin, a Peptide Purified from the Medicinal Mushroom Cordyceps sinensis, on Diabetic Osteopenia in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 24174985
- PMCID: PMC3794654
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/985636
The Protective Effect of Cordymin, a Peptide Purified from the Medicinal Mushroom Cordyceps sinensis, on Diabetic Osteopenia in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
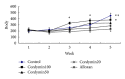
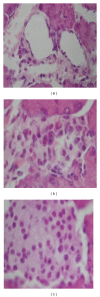
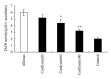
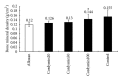
The aim of this study was to investigate the protective effect of cordymin on diabetic osteopenia in alloxan-induced diabetic rats and the possible mechanisms involved. The diabetic rats received daily intraperitoneal injection with cordymin (20, 50, and 100 mg/kg/day) for 5 weeks. Cordymin could restore the circulating blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP), tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), and insulin levels in a dose-dependent manner. Also, the treatment of diabetic rats with cordymin could partially reverse the β cells death and decrease the total antioxidant status (TAOS) in the diabetic rats. The results may directly and indirectly account for the possible mechanism of the beneficial effect of cordymin on diabetic osteopenia, which was confirmed with the increased bone mineral content (BMC) and bone mineral density (BMD) in diabetic rats (P < 0.05). All those findings indicate that cordymin may play a protective role in diabetic osteoporosis.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang X, Shi P, Cao S, Yu H, Azad J, Ling S. Expression changes of transforming growth factor-beta1 and thrombospondin-1 in cavernous tissues of diabetic rats. Urologia Internationalis. 2010;84(2):221–225. - PubMed
-
- Del Canizo Gomez FJ, Fernandez Perez C, Moreno Ruiz I, et al. Microvascular complications and risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocrinología y Nutrición. 2011;58(4):163–168. - PubMed
-
- Lu B, Gong W, Yang Z, et al. An evaluation of the diabetic kidney disease definition in chinese patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus. The Journal of International Medical Research. 2009;37(5):1493–1500. - PubMed
-
- Atsumi H, Kitada M, Kanasaki K, Koya D. Reversal of redox-dependent inhibition of diacylglycerol kinase by antioxidants in mesangial cells exposed to high glucose. Molecular Medicine Reports. 2011;4(5):923–927. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto M, Yamaguchi T, Yamauchi M, Kaji H, Sugimoto T. Diabetic patients have an increased risk of vertebral fractures independent of BMD or diabetic complications. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2009;24(4):702–709. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

