Pulsed radiofrequency neuromodulation for the treatment of saphenous neuralgia
- PMID: 24175030
- PMCID: PMC3809441
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.2.136
Pulsed radiofrequency neuromodulation for the treatment of saphenous neuralgia
Abstract
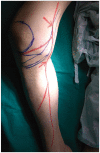
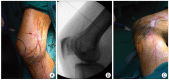
A 65-year-old male presented with pain in his right medial calf. An imaging study revealed no acute lesions, and a diagnosis of saphenous neuralgia was made by a nerve conduction study. He received temporary pain relief with saphenous nerve blocks twice in a one-week interval. Pulsed radiofrequency neuromodulation reduced pain to 10% of the maximal pain intensity. At 6 months after the procedure, the pain intensity was not aggravated even without medication. Pulsed radiofrequency neuromodulation of the saphenous nerve may offer an effective and minimally invasive treatment for patients with saphenous neuralgia who are refractory to conservative management.
Keywords: Neuromodulation; Pulsed radiofrequency; Saphenous neuralgia.
Figures
References
-
- Bertram C, Porsch M, Hackenbroch MH, Terhaag D. Saphenous neuralgia after arthroscopically assisted anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with a semitendinosus and gracilis tendon graft. Arthroscopy. 2000;16:763–766. - PubMed
-
- Cahana A, Vutskits L, Muller D. Acute differential modulation of synaptic transmission and cell survival during exposure to pulsed and continuous radiofrequency energy. J Pain. 2003;4:197–202. - PubMed
-
- Cosman ER, Jr, Cosman ER., Sr Electric and thermal field effects in tissue around radiofrequency electrodes. Pain Med. 2005;6:405–424. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

