Full rehabilitation with nobel clinician(®) and procera implant bridge(®): case report
- PMID: 24175051
- PMCID: PMC3808939
Full rehabilitation with nobel clinician(®) and procera implant bridge(®): case report
Abstract
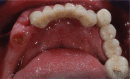
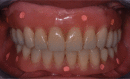
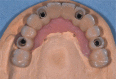
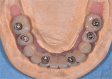
Implant surgery has been changing in different ways following improvements of computer technologies. Since its beginning, according to the original procedures of Branemårk system implants, guide-lines in implants-supported prosthetic rehabilitation have been founding on the placement of fixtures in a fairly upright position, after maxillary sinus floor elevation; while in the case of interforaminal rehabilitation, an upright distal implant may need to be placed anterior to the mental foramina without nerve damage (although the consequence would have been bilateral cantilevers to provide good chewing capacity). Some authors have proposed engaging the molar/tuberosity area: Bahat and Venturelli demonstrated these areas reliable and predictable alternative to distal cantilever prostheses or sinus elevation procedures. In recent years, the immediate loading of tilted implants with a provisional restoration has been proposed for the treatment of the atrophic maxilla. Tilted posterior implants in either arches could avoid (cantilever length) and provide to a better load distribution. Further studies have showed excellent outcomes for both tilted and axial implants; indeed this protocol allows to use longer implants, improve bone anchorage and avoid bone grafting procedures. Malò at al., in a retrospective clinical study, showed important results using two posterior tilted implants and two anterior non-tilted ones in the so-called All-on-four technique (Nobel Biocare, Göteborg, Sweden). Instead of the great loss of bone (amount and quality) in long-term edentuly the clinically documented computer-guided implantology software is able, through posterior tilted implants, to improve load distribution. Many authors have reported reduced surgical invasion (sinus grafting surgery is needless), shorter treatment time, lower cost, natural aesthetic profiles and functional bite.
Keywords: computer guided flapless implant placement; dental implants; immediate loading; prosthetic rehabilitation.
Figures

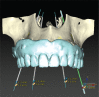

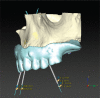
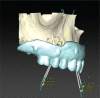

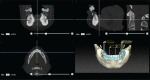
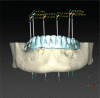
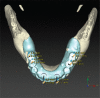



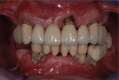
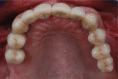


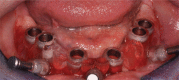
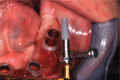
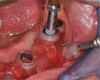
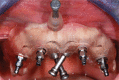
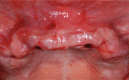
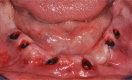
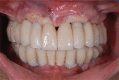
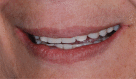
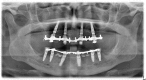
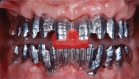
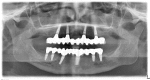

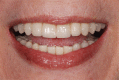
References
-
- Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointe-grated oral implants. (I). Success criteria and epidemiology. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998;106:527–551. - PubMed
-
- Cricchio G, Lundgren S. Donor site morbidity in two different approaches to anterior iliac crest bone harvesting. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5:161–169. - PubMed
-
- Nkenke E, Schultze-Mosgau S, Radespiel-Troger M, Kloss F, Neukam FW. Morbidity of harvesting of chin grafts: a prospective study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12:495–502. - PubMed
-
- Clavero J, Lundgren S. Ramus or chin grafts for maxillary sinus inlay and local onlay augmentation: comparison of donor site morbidity and complications. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003;5:154–160. - PubMed
-
- Lundgren S, Nystrom E, Nilson H, Gunne J, Lindhagen O. Bone grafting to the maxillary sinuses, nasal floor and anterior maxilla in the atrophic edentulous maxilla. A two-stage technique. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;26:428–434. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
