Adrenomedullin and cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 24175071
- PMCID: PMC3738363
- DOI: 10.1258/cvd.2012.012003
Adrenomedullin and cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
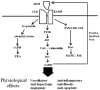
The cardiovascular system is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, nitric oxide (NO) and other factors including neuropeptides. Research in neurohumoral factors has led to the development of many cardiovascular drugs. Adrenomedullin (ADM), initially isolated from the adrenal gland, has diverse physiological and pathophysiological functions in the cardiovascular system. It is produced in many organs and tissues including the vasculature. ADM has numerous actions, including vasodilation, natriuresis, antiapoptosis and stimulation of NO production. It might play a protective role in various cardiovascular pathologies, and its plasma level is elevated in patients with hypertension and heart failure. Administration of ADM is a possible therapeutic approach for treating cardiovascular diseases. A number of studies have investigated the infusion of ADM in humans, which seems to be benficial in heart failure and myocardial infarction. Instead of ADM infusion, augmentation of its endogenous level is another possible strategy. Gene therapy is feasible in animal models, but its application in humans is limited. At present, the most promising clinical application of ADM is the use of the plasma level of mid-regional proadrenomedullin as a biomarker in cardiovascular diseases. It is a good marker of prognosis and survival in patients with coronary aretery disease or heart failure.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adrenomedullin augments the neurohumoral response to haemorrhage in non-pregnant but not in pregnant sheep.J Endocrinol. 2001 Nov;171(2):363-71. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1710363. J Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11691657
-
Potent and long-lasting vasodilatory effects of adrenomedullin in humans. Comparisons between normal subjects and patients with chronic heart failure.Circulation. 1997 Mar 4;95(5):1214-21. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.5.1214. Circulation. 1997. PMID: 9054852
-
Adrenomedullin--what do we know 10 years since its discovery?Pol J Pharmacol. 2004 Jan-Feb;56(1):5-27. Pol J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15047974 Review.
-
Human coronary arteriolar dilation to adrenomedullin: role of nitric oxide and K(+) channels.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000 Dec;279(6):H2620-6. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.2000.279.6.H2620. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11087213
-
[Adrenomedullin].Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 1999;53(1):99-123. Postepy Hig Med Dosw. 1999. PMID: 10352550 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Epicardial Fat: Physiological, Pathological, and Therapeutic Implications.Cardiol Res Pract. 2016;2016:1291537. doi: 10.1155/2016/1291537. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Cardiol Res Pract. 2016. PMID: 27213076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison between men and women of volume regulating hormones and aquaporin-2 excretion following graded central hypovolemia.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019 Mar;119(3):633-643. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-4053-2. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30564880
-
Sandwich immunoassay for adrenomedullin precursor and its practical application.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 15;14(1):28091. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79542-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39543387 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertensive Heart Disease: A Narrative Review Series-Part 3: Vasculature, Biomarkers and the Matrix of Hypertensive Heart Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 16;13(2):505. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020505. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38256639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Value of Immune-Related Genes in Kawasaki Disease.Front Genet. 2021 Dec 10;12:763496. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.763496. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34956318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nishikimi T Adrenomedullin in Cardiovascular Disease. New York: SAGE Publications, 2005.
-
- Kato J, Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Eto T Receptors for adrenomedullin in human vascular endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol Mol Pharmacol 1995;289:383–5 - PubMed
-
- Bunton DC, Petrie MC, Hillier C, Johnston F, McMurray JJV The clinical relevance of adrenomedullin: a promising profile? Pharmacol Ther 2004;103:179–201 - PubMed
-
- Juaneda C, Dumont Y, Chabot J, Fournier A, Quirion R Adrenomedullin receptor binding sites in rat brain and peripheral tissues. Eur J Pharmacol 2003;474:165–74 - PubMed
-
- Cheung BM, Tang F Adrenomedullin: exciting new horizons. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov 2012;6:4–17 - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

