Contrast-induced acute kidney injury following iodine opacification other than by intravascular injection
- PMID: 24175084
- PMCID: PMC3811973
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfs102
Contrast-induced acute kidney injury following iodine opacification other than by intravascular injection
Abstract
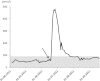
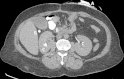
Contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) classically occurs following the intravascular administration of iodinated contrast medium (CM). However, some cases of iodine-induced nephrotoxicity have been reported in patients who did not receive intravascular CM, as a consequence of iodine absorption through mucosae, burned skin or interstitial tissues. Recently, we observed the first case of CI-AKI occurring after an enteroclysis without any direct intravascular injection of CM. Here, we report this case, and review other clinical situations in which renal toxicity has been reported following the non-intravascular use of iodinated compounds.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; acute renal failure; contrast-induced acute kidney injury; enteroclysis; iodine toxicity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intravascular Iodinated Contrast Is an Independent Cause of Acute Kidney Injury Following Coronary Angiography.South Med J. 2019 Oct;112(10):541-546. doi: 10.14423/SMJ.0000000000001029. South Med J. 2019. PMID: 31583416
-
Incidence of nonconfounded post-computed tomography acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients with stable renal function receiving intravenous iodinated contrast material.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2014 Sep-Oct;43(5):237-41. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24909428
-
Contrast-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: Advances and Challenges.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Feb 15;15:1537-1546. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S341072. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35210826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nephrotoxicity of iodinated contrast media: From pathophysiology to prevention strategies.Eur J Radiol. 2019 Jul;116:231-241. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 15. Eur J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31054788 Review.
-
Risk of renal events following intravenous iodinated contrast material administration among inpatients admitted with cancer a retrospective hospital claims analysis.Cancer Imaging. 2018 Aug 24;18(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s40644-018-0159-3. Cancer Imaging. 2018. PMID: 30143056 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Povidone-iodine toxicity in a child posted for laparoscopic removal of hepatic and renal hydatid cysts.Indian J Anaesth. 2015 Feb;59(2):135-6. doi: 10.4103/0019-5049.151385. Indian J Anaesth. 2015. PMID: 25788754 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A case of severe nephrotoxicity associated with long-term dietary supplement use.Clin Nephrol Case Stud. 2017 Aug 2;5:42-7. doi: 10.5414/CNCS109180. Online ahead of print. Clin Nephrol Case Stud. 2017. PMID: 28766491 Free PMC article.
-
The downside of antimicrobial agents for wound healing.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Jan;38(1):39-54. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-3393-5. Epub 2018 Oct 5. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30291466 Review.
-
Contrast induced nephropathy in women with infertility undergoing hysterosalpingography.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024 Dec 19;22(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12958-024-01334-3. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39702139 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicological evaluation of repeated administration of povidone iodine in cockerels.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Mar 1;9:293-297. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.02.010. eCollection 2022. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35284237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lameire N. Contrast-induced nephropathy—prevention and risk reduction. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:11–23. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfl215. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Solomon R. Contrast media nephropathy—how to diagnose and how to prevent? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22:1812–1815. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm207. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Canales CO, Smith GH, Robinson JC, et al. Brief recordings. Acute renal failure after the administration of iopanoic acid as a cholecystographic agent. N Engl J Med. 1969;281:89–91. doi:10.1056/NEJM196907102810207. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gregory MC. Acute renal failure after percutaneous cholangiography. Arch Intern Med. 1984;144:1288–1289. doi:10.1001/archinte.1984.00350180236035. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kabza R, Dyktynski P. 2 cases of acute renal failure following cholangiography through the Kehr's drain. Wiad Lek. 1969;22:1319–1321. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources