Photoinitiated polymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate by riboflavin/triethanolamine in aqueous solution: a kinetic study
- PMID: 24175102
- PMCID: PMC3794564
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/958712
Photoinitiated polymerization of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate by riboflavin/triethanolamine in aqueous solution: a kinetic study
Abstract
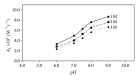
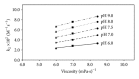
The polymerization of 1-3 M 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) initiated by riboflavin/triethanolamine system has been studied in the pH range 6.0-9.0. An approximate measure of the kinetics of the reaction during the initial stages (~5% HEMA conversion) has been made to avoid the effect of any variations in the volume of the medium. The concentration of HEMA in polymerized solutions has been determined by a UV spectrophotometric method at 208 nm with a precision of ±3%. The initial rate of polymerization of HEMA follows apparent first-order kinetics and the rates increase with pH. This may be due to the presence of a labile proton on the hydroxyl group of HEMA. The second-order rate constants for the interaction of triethanolamine and HEMA lie in the range of 2.36 to 8.67 × 10(-2) M(-1) s(-1) at pH 6.0-9.0 suggesting an increased activity with pH. An increase in the viscosity of HEMA solutions from 1 M to 3 M leads to a decrease in the rate of polymerization probably as a result of the decrease in the reactivity of the flavin triplet state. The effect of pH and viscosity of the medium on the rate of reaction has been evaluated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Degradation kinetics of methacrylated dextrans in aqueous solution.J Pharm Sci. 1997 Apr;86(4):413-7. doi: 10.1021/js9604220. J Pharm Sci. 1997. PMID: 9109041
-
Effect of caffeine complexation on the photolysis of riboflavin in aqueous solution: a kinetic study.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009 Dec;57(12):1363-70. doi: 10.1248/cpb.57.1363. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2009. PMID: 19952445
-
Photolysis of riboflavin in aqueous solution: a kinetic study.Int J Pharm. 2004 Aug 6;280(1-2):199-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.05.020. Int J Pharm. 2004. PMID: 15265559
-
Effect of borate buffer on the photolysis of riboflavin in aqueous solution.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2008 Nov 13;93(2):82-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2008.07.005. Epub 2008 Jul 29. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2008. PMID: 18760621
-
Study of polymerization of acrylic bone cement: effect of HEMA and EGDMA.J Biomed Mater Res. 1998 Spring;43(1):54-61. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4636(199821)43:1<54::aid-jbm6>3.0.co;2-l. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998. PMID: 9509344
Cited by
-
Polymerization Assisted by Upconversion Nanoparticles under NIR Light.Molecules. 2019 Jul 5;24(13):2476. doi: 10.3390/molecules24132476. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31284486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mitra SB. Adhesion to dentin and physical properties of a light-cured glass-ionomer liner/base. Journal of Dental Research. 1991;70(1):72–74. - PubMed
-
- Atai M, Ahmadi M, Babanzadeh S, Watts DC. Synthesis, characterization, shrinkage and curing kinetics of a new low-shrinkage urethane dimethacrylate monomer for dental applications. Dental Materials. 2007;23(8):1030–1041. - PubMed
-
- Moshaverinia A, Roohpour N, Darr JA, Rehman IU. Synthesis of a proline-modified acrylic acid copolymer in supercritical CO2 for glass-ionomer dental cement applications. Acta Biomaterialia. 2009;5(5):1656–1662. - PubMed
-
- Moshaverinia A, Roohpour N, Darr JA, Rehman IU. Synthesis and characterization of a novel N-vinylcaprolactam-containing acrylic acid terpolymer for applications in glass-ionomer dental cements. Acta Biomaterialia. 2009;5(6):2101–2108. - PubMed
-
- Moshaverinia A, Roohpour N, Billington RW, Darr JA, Rehman IU. Synthesis of N-vinylpyrrolidone modified acrylic acid copolymer in supercritical fluids and its application in dental glass-ionomer cements. Journal of Materials Science. 2008;19(7):2705–2711. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

