Frataxin mRNA isoforms in FRDA patients and normal subjects: effect of tocotrienol supplementation
- PMID: 24175286
- PMCID: PMC3794619
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/276808
Frataxin mRNA isoforms in FRDA patients and normal subjects: effect of tocotrienol supplementation
Abstract
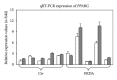
Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA) is caused by deficient expression of the mitochondrial protein frataxin involved in the formation of iron-sulphur complexes and by consequent oxidative stress. We analysed low-dose tocotrienol supplementation effects on the expression of the three splice variant isoforms (FXN-1, FXN-2, and FXN-3) in mononuclear blood cells of FRDA patients and healthy subjects. In FRDA patients, tocotrienol leads to a specific and significant increase of FXN-3 expression while not affecting FXN-1 and FXN-2 expression. Since no structural and functional details were available for FNX-2 and FXN-3, 3D models were built. FXN-1, the canonical isoform, was then docked on the human iron-sulphur complex, and functional interactions were computed; when FXN-1 was replaced by FXN-2 or FNX-3, we found that the interactions were maintained, thus suggesting a possible biological role for both isoforms in human cells. Finally, in order to evaluate whether tocotrienol enhancement of FXN-3 was mediated by an increase in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARG), PPARG expression was evaluated. At a low dose of tocotrienol, the increase of FXN-3 expression appeared to be independent of PPARG expression. Our data show that it is possible to modulate the mRNA expression of the minor frataxin isoforms and that they may have a functional role.
Figures




References
-
- de Michele G, Perrone F, Filla A, et al. Age of onset, sex, and cardiomyopathy as predictors of disability and survival in Friedreich’s disease: a retrospective study on 119 patients. Neurology. 1996;47(5):1260–1264. - PubMed
-
- Gellera C, Castellotti B, Mariotti C, et al. Frataxin gene point mutations in Italian friedreich ataxia patients. Neurogenetics. 2007;8(4):289–299. - PubMed
-
- Campuzano V, Montermini L, Moltò MD, et al. Friedreich’s ataxia: autosomal recessive disease caused by an intronic GAA triplet repeat expansion. Science. 1996;271(5254):1423–1427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

