Novel microwell assay with high throughput and minimum consumption for organic solvents in the charge transfer-based spectrophotometric determination of clarithromycin in pharmaceutical formulations
- PMID: 24176103
- PMCID: PMC3817450
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-172
Novel microwell assay with high throughput and minimum consumption for organic solvents in the charge transfer-based spectrophotometric determination of clarithromycin in pharmaceutical formulations
Abstract
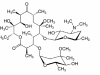
Background: Clarithromycin (CLM) is a semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic with a broad antibacterial spectrum. It has a potent activity against Myc. Pneumonia, Legionella Spp., H. Influenza, and Mor. Catarrhalis. It is also used for prevention and treatment of disseminated M. Avium infections in patients with AIDS. The therapeutic importance and wide use of CLM promotes the growing interest in developing proper methods for its determination in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations.
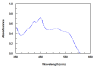
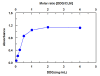
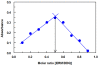
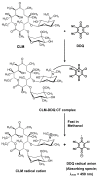
Results: The present study describes the development and validation of a novel assay that can increase the throughput and reduce the consumption of organic solvents in the charge transfer (CT)-based spectrophotometric determination of CLM. In this assay, the CT reaction between CLM as n-electron donor and 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (DDQ) as a π-electron acceptor was performed in the 96-microwells of an assay plate. The color signals of the CT complex were measured at 450 nm by microwell-plate absorbance reader. The linear range of the assay was 20-850 μg mL-1. The limits of detection and quantitation were 15.5 and 51.2 μg mL-1, respectively. The proposed assay gave very high precisions; the relative standard deviation (RSD) values did not exceed 1.82%.
Conclusions: The assay described herein has a high throughput property that facilitates the processing of large number of samples in a reasonable time. As well, it consumes minimum volumes of organic solvents, thus it significantly reduces the exposures of the analysts to the toxic effects of organic solvents, and reduce the analysis cost by 50-folds. The results demonstrated that the proposed assay has great practical value in the routine analysis of CLM in quality control laboratories.
Figures
References
-
- Bahal N, Nahata MC. The new macrolide antibiotics: azithromycin, clarithromycin, dirithromycin. Ann Pharmacother. 1992;26:46–55. - PubMed
-
- Parfitt K. In: Martindale The Complete Drug Reference. 33. Sweetman SC, editor. London: Pharmaceutical Press; 2002. p. 186.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

