killerFLIP: a novel lytic peptide specifically inducing cancer cell death
- PMID: 24176852
- PMCID: PMC3920952
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.401
killerFLIP: a novel lytic peptide specifically inducing cancer cell death
Abstract
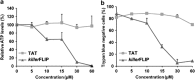
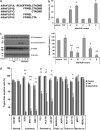
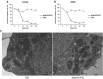
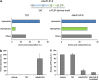
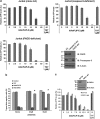
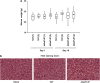
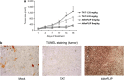
One of the objectives in the development of effective cancer therapy is induction of tumor-selective cell death. Toward this end, we have identified a small peptide that, when introduced into cells via a TAT cell-delivery system, shows a remarkably potent cytoxicity in a variety of cancer cell lines and inhibits tumor growth in vivo, whereas sparing normal cells and tissues. This fusion peptide was named killerFLIP as its sequence was derived from the C-terminal domain of c-FLIP, an anti-apoptotic protein. Using structure activity analysis, we determined the minimal bioactive core of killerFLIP, namely killerFLIP-E. Structural analysis of cells using electron microscopy demonstrated that killerFLIP-E triggers cell death accompanied by rapid (within minutes) plasma membrane permeabilization. Studies of the structure of the active core of killerFLIP (-E) indicated that it possesses amphiphilic properties and self-assembles into micellar structures in aqueous solution. The biochemical properties of killerFLIP are comparable to those of cationic lytic peptides, which participate in defense against pathogens and have also demonstrated anticancer properties. We show that the pro-cell death effects of killerFLIP are independent of its sequence similarity with c-FLIPL as killerFLIP-induced cell death was largely apoptosis and necroptosis independent. A killerFLIP-E variant containing a scrambled c-FLIPL motif indeed induced similar cell death, suggesting the importance of the c-FLIPL residues but not of their sequence. Thus, we report the discovery of a promising synthetic peptide with novel anticancer activity in vitro and in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Alderton GK, Bordon Y. Tumour immunotherapy--leukocytes take up the fight. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12:237. - PubMed
-
- Vander Heiden MG. Targeting cancer metabolism: a therapeutic window opens. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:671–684. - PubMed
-
- Tu Z, Hao J, Kharidia R, Meng XG, Liang JF. Improved stability and selectivity of lytic peptides through self-assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361:712–717. - PubMed
-
- Papo N, Shai Y. New lytic peptides based on the D,L-amphipathic helix motif preferentially kill tumor cells compared to normal cells. Biochemistry. 2003;42:9346–9354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

