Synthesis of a probe for monitoring HSV1-tk reporter gene expression using chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI
- PMID: 24177294
- PMCID: PMC3870049
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2013.140
Synthesis of a probe for monitoring HSV1-tk reporter gene expression using chemical exchange saturation transfer MRI
Abstract
In experiments involving transgenic animals or animals treated with transgenic cells, it is important to have a method to monitor the expression of the relevant genes longitudinally and noninvasively. An MRI-based reporter gene enables monitoring of gene expression in the deep tissues of living subjects. This information can be co-registered with detailed high-resolution anatomical and functional information. We describe here the synthesis of the reporter probe, 5-methyl-5,6-dihydrothymidine (5-MDHT), which can be used for imaging of the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase (HSV1-tk) reporter gene expression in rodents by MRI. The protocol also includes data acquisition and data processing routines customized for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) contrast mechanisms. The dihydropyrimidine 5-MDHT is synthesized through a catalytic hydrogenation of the 5,6-double bond of thymidine to yield 5,6-dihydrothymidine, which is methylated on the C-5 position of the resulting saturated pyrimidine ring. The synthesis of 5-MDHT can be completed within 5 d, and the compound is stable for more than 1 year.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
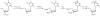


References
-
- Culver KW, et al. In vivo gene transfer with retroviral vector-producer cells for treatment of experimental brain tumors. Science. 1992;256:1550–1552. - PubMed
-
- Tjuvajev JG, et al. Imaging herpes virus thymidine kinase gene transfer and expression by positron emission tomography. Cancer Res. 1998;58:4333–4341. - PubMed
-
- Tjuvajev JG, et al. Noninvasive imaging of herpes virus thymidine kinase gene transfer and expression: a potential method for monitoring clinical gene therapy. Cancer Res. 1996;56:4087–4095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

