Relationship between oral health and its impact on the quality life of Alzheimer's disease patients: a supportive care trial
- PMID: 24179569
- PMCID: PMC3798211
Relationship between oral health and its impact on the quality life of Alzheimer's disease patients: a supportive care trial
Abstract
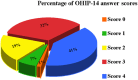
Dental infections have recently been related with a possible risk factor for Neurodegenerative pathologies like Alzheimer's disease (AD). Even if there are no specific studies investigating orofacial pain in this patient group, dental health is known to be a potential cause of pain and to influence quality of life and disease progression. The aim of this study was to investigate how the AD patients' oral health status may influence their quality of life. 158 patients affected by AD were evaluated using Decayed Missed Filled Teeth (DMFT), Oral Health Impact Profile-14 (OHIP-14) and Clinical Investigation consisting in the detection of cavities and measurement of the probing depth in each patient; other parameters like gingival bleeding, biofilm index and tooth mobility degree test have been recorded. The ratio between diagnosis of periodontal disease and impact on quality of life was significant in individuals with periodontitis (p < 0.001) and missed filled teeth. Gingival bleeding, and probing depth > 4 mm were associated with intensely negative impact on quality of life (p = 0.013, p < 0.001, and p = 0.012 respectively). Moreover, the absence of more than 2 molar teeth increases the chewing inability decreasing the patient quality of life.
Conclusion: It was observed a correlation between the age and the high index of pathologies analyzed, due to the progressive nature of the disease. Concepts of health and disease determined by clinical diagnostic criteria may influence the assessment of the impact of periodontal disease on Alzheimer's quality of life.
Keywords: Alzheimer; OHIP-14; health; oral.
Figures
References
-
- Schembri A, Fiske J. The implications of visual impairment in an elderly population in recognizing oral disease and maintaining oral health. Spec Care Dentist. 2001 Nov-Dec;21:222–6. - PubMed
-
- Henry RG. Neurological disorders in dentistry: managing patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Indiana Dent Assoc. 1997-1998;76:51–7. - PubMed
-
- Ghezzi EM, Ship JA. Dementia and oral health. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2000;89:2–5. - PubMed
-
- Schembri A, Fiske J. The implications of visual impairment in an elderly population in recognizing oral disease and maintaining oral health. Spec Care Dentist. 2001 Nov-Dec;21:222–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources