Presence of disease specific autoantibodies against liver sinusoidal cells in primary biliary cirrhosis
- PMID: 24179616
- PMCID: PMC3812459
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i10.568
Presence of disease specific autoantibodies against liver sinusoidal cells in primary biliary cirrhosis
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the presence of autoantibodies directed against liver sinusoidal cells in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC).
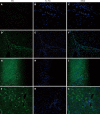
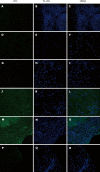
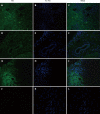
Methods: Liver biopsies from 21 PBC patients were studied and compared with 12 liver biopsies from disease controls [3 patients with hepatitis B (HBV) virus, 3 patients with hepatitis C virus (HCV), 3 patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and 3 patients with acute alcoholic hepatitis (AAH)]. As healthy controls, we used tissue specimens adjacent to metastatic liver adenocarcinoma. Normal serum was taken from staff members of the unit. The determination of the cell type targeted by autoantibodies present in the patients sera was performed by indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) analysis using paraffin-embedded liver sections as a substrate. Sera from homologous or heterologous PBC patients or sera from the disease control group were used as primary antibodies. The presence of autoantibodies was identified using confocal microscopy.
Results: In total, 18/21 (85.7%) PBC patients exhibited positive staining in the sinusoidal cells, 10/21 (47.6%) in lymphocytes, 8/21 (38%) in cholangiocytes and 7/21 (33.3%) in hepatocytes, when homologous serum and fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated immunoglobulin type G (IgG) secondary antibody were used. PBC sections incubated with heterologous PBC serum showed reduced staining (20% for sinusoidal cells, 20% for lymphocytes, 20% for cholangiocytes and 13.3% for hepatocytes). When IgM immunoglobulin, instead of IgG, was used as secondary antibody, positive staining was observed in 75% of lymphocytes, 62.5% of cholangiocytes, 37.5% of hepatocytes and 50% of the sinusoidal cells with a much stronger staining intensity. No staining was observed when either normal or PBC sera were used as a primary antibody on liver sections from the disease control group. When PBC sera were incubated with healthy control sections, weak positive staining of cholangiocytes was observed in 3/21 (14.3%) PBC serum samples. Steatohepatitis serum on PBC sections gave a positive staining of some hepatocytes and lymphocytes but no staining on viral hepatitis sections. Incubation with HBV sera stained some hepatocytes, cholangiocytes and intra-sinusoidal or portal lymphocytes of PBC, HBV and AAH patients but not HCV patients.
Conclusion: In this study, for the first time in diseased liver tissue, we have demonstrated that a large proportion of PBC patients have disease specific autoantibodies against liver sinusoidal cells.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; Cholangiocytes; Liver tissue; Primary biliary cirrhosis; Sinusoidal cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased ΤGF-β3 in primary biliary cirrhosis: an abnormality related to pathogenesis?World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Oct 28;16(40):5057-64. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i40.5057. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20976842 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of antibodies to calreticulin of the IgA class in primary biliary cirrhosis: a possible role of gut-derived bacterial antigens in its aetiology?Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999 Jun;34(6):623-8. doi: 10.1080/003655299750026100. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1999. PMID: 10440614
-
Clinical significance of positive immunoblotting but negative immunofluorescence for antimitochondrial antibodies in patients with liver diseases other than primary biliary cirrhosis.Autoimmunity. 2002 Mar;35(2):135-41. doi: 10.1080/08916930290016556. Autoimmunity. 2002. PMID: 12071436
-
Overcoming a "probable" diagnosis in antimitochondrial antibody negative primary biliary cirrhosis: study of 100 sera and review of the literature.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012 Jun;42(3):288-97. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8234-y. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21188646 Review.
-
Disease-specific autoantibodies in primary biliary cirrhosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2011 Mar 18;412(7-8):502-12. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2010.12.019. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Clin Chim Acta. 2011. PMID: 21185272 Review.
Cited by
-
Primary biliary cirrhosis: From bench to bedside.World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Aug 6;6(3):32-58. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v6.i3.32. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26261733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunofluorescence identifies distinct subsets of endothelial cells in the human liver.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 13;7:44356. doi: 10.1038/srep44356. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28287163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Selmi C, Invernizzi P, Zuin M, Podda M, Seldin MF, Gershwin ME. Genes and (auto)immunity in primary biliary cirrhosis. Genes Immun. 2005;6:543–556. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan MM, Gershwin ME. Primary biliary cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1261–1273. - PubMed
-
- Surh CD, Ahmed-Ansari A, Gershwin ME. Comparative epitope mapping of murine monoclonal and human autoantibodies to human PDH-E2, the major mitochondrial autoantigen of primary biliary cirrhosis. J Immunol. 1990;144:2647–2652. - PubMed
-
- Tsuneyama K, Van De Water J, Van Thiel D, Coppel R, Ruebner B, Nakanuma Y, Dickson ER, Gershwin ME. Abnormal expression of PDC-E2 on the apical surface of biliary epithelial cells in patients with antimitochondrial antibody-negative primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1995;22:1440–1446. - PubMed
-
- Yip TT, Van de Water J, Gershwin ME, Coppel RL, Hutchens TW. Cryptic antigenic determinants on the extracellular pyruvate dehydrogenase complex/mimeotope found in primary biliary cirrhosis. A probe by affinity mass spectrometry. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:32825–32833. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

