Analysis of the morphometry and variations in the extensor digitorum brevis muscle: an anatomic guide for muscle flap and tendon transfer surgical dissection
- PMID: 24179695
- PMCID: PMC3811858
- DOI: 10.5115/acb.2013.46.3.198
Analysis of the morphometry and variations in the extensor digitorum brevis muscle: an anatomic guide for muscle flap and tendon transfer surgical dissection
Abstract
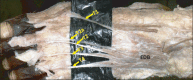
The extensor digitorum brevis muscle (EDB) is a practical option for use as an island flap or free flap when reconstructing soft tissue defects in the ankle as well as in the entire lower limb. It is frequently used to correct crossover toe deformity and other painful toe disorders. We evaluated the morphometry of the EDB in 44 formalin-fixed limbs. Length and width of the muscles were measured. Surface area was calculated as the product of length and width of the muscle. The length of each tendon was also measured from its origin to the point of distal attachment. Presence of any additional tendons was noted. Mean length, width, and surface area of the muscle were 7.39±0.71 cm, 4.1±0.37 cm, and 30.5±4.78 cm(2) on the right side and 7.2±0.84 cm, 3.9±0.37 cm, and 28.4±5.35 cm(2) on the left side, respectively. Morphometry of the tendons revealed that the tendon of the great toe had the highest mean length (9.5 cm) and the tendon of the fourth toe had the lowest mean length (6.3 cm). Four of the limbs studied (9.09%) had only three tendons. Three of the limbs studied (6.81%) had five tendons, and in one exceptional case (2.27%), six tendons were detected. These observations have significant value and are applicable to plastic and orthopedic surgery.
Keywords: Crossover toe deformity; Extensor digitorum brevis; Morphometry; Reconstruction; Tendon transfer.
Figures




References
-
- Standring S. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 39th ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; 2005. pp. 1536–1537.
-
- Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AM. Clinically oriented anatomy. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippencott, Williams & Wilkins; 2009. pp. 612–614.
-
- Moore KL, Persaud TV. The developing human: clinically oriented embryology. 6th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2002. pp. 612–614.
-
- Baltensperger MM, Ganzoni N, Jirecek V, Meyer VE. The extensor digitorum brevis island flap: possible applications based on anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;101:107–113. - PubMed
-
- del Piñal F, Herrero F. Extensor digitorum brevis free flap: anatomic study and further clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;105:1347–1356. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
