Computational analysis reveals increased blood deposition following repeated mild traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 24179733
- PMCID: PMC3757717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nicl.2012.08.001
Computational analysis reveals increased blood deposition following repeated mild traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) has become an increasing public health concern as subsequent injuries can exacerbate existing neuropathology and result in neurological deficits. This study investigated the temporal development of cortical lesions using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess two mTBIs delivered to opposite cortical hemispheres. The controlled cortical impact model was used to produce an initial mTBI on the right cortex followed by a second injury induced on the left cortex at 3 (rmTBI 3d) or 7 (rmTBI 7d) days later. Histogram analysis was combined with a novel semi-automated computational approach to perform a voxel-wise examination of extravascular blood and edema volumes within the lesion. Examination of lesion volume 1d post last injury revealed increased tissue abnormalities within rmTBI 7d animals compared to other groups, particularly at the site of the second impact. Histogram analysis of lesion T2 values suggested increased edematous tissue within the rmTBI 3d group and elevated blood deposition in the rm TBI 7d animals. Further quantification of lesion composition for blood and edema containing voxels supported our histogram findings, with increased edema at the site of second impact in rmTBI 3d animals and elevated blood deposition in the rmTBI 7d group at the site of the first injury. Histological measurements revealed spatial overlap of regions containing blood deposition and microglial activation within the cortices of all animals. In conclusion, our findings suggest that there is a window of tissue vulnerability where a second distant mTBI, induced 7d after an initial injury, exacerbates tissue abnormalities consistent with hemorrhagic progression.
Keywords: DTI, diffusion tensor imaging; Edema; FA, fractional anisotropy; HPC, hemorrhagic progression of the contusion; Hemorrhagic progression; Histogram; MD, mean diffusivity; Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging; T2.
Figures
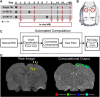
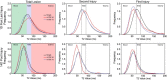
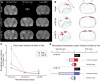


References
-
- Alahmadi H., Vachhrajani S., Cusimano M.D. The natural history of brain contusion: an analysis of radiological and clinical progression. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2010;112:1139–1145. - PubMed
-
- Belanger H.G., Spiegel E., Vanderploeg R.D. Neuropsychological performance following a history of multiple self-reported concussions: a meta-analysis. Journal of International Neuropsychological Society. 2010;16:262–267. - PubMed
-
- Belayev L., Obenaus A., Zhao W., Saul I., Busto R., Wu C., Vigdorchik A., Lin B., Ginsberg M.D. Experimental intracerebral hematoma in the rat: characterization by sequential magnetic resonance imaging, behavior, and histopathology. Effect of albumin therapy. Brain Research. 2007;1157:146–155. - PubMed
-
- Benson R.R., Meda S.A., Vasudevan S., Kou Z., Govindarajan K.A., Hanks R.A., Millis S.R., Makki M., Latif Z., Coplin W., Meythaler J., Haacke E.M. Global white matter analysis of diffusion tensor images is predictive of injury severity in traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma. 2007;24:446–459. - PubMed
-
- Boje K.M., Arora P.K. Microglial-produced nitric oxide and reactive nitrogen oxides mediate neuronal cell death. Brain Research. 1992;587:250–256. - PubMed

