High expression of ezrin predicts poor prognosis in uterine cervical cancer
- PMID: 24182314
- PMCID: PMC4228363
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-520
High expression of ezrin predicts poor prognosis in uterine cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: Ezrin, a member of the ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) protein family, plays a pivotal role in tumor invasion and metastasis. This study is aimed to investigate the clinicopathological significance of upregulated ezrin protein expression in uterine cervical cancers.
Methods: Immunohistochemical staining of ezrin protein was performed on uterine cervical cancer specimens from 235 patients. For comparison, 239 cases of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), 17 cases of cervical glandular intraepithelial neoplasia (CGIN) and 52 normal cervix samples were also included. qRT-PCR was performed on fresh tissues to detect ezrin mRNA expression levels. HPV infection statuses were genotyped by oligonucleotide microarray, and 10-year survival rates were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method for 109 cervical cancer patients.
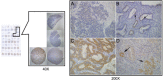
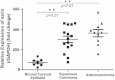
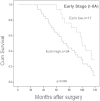
Results: Apical membranous distribution of ezrin protein was only observed in normal cervical glands, while perinuclear staining was only observed in cervical cancers. Strong cytoplasmic and diffuse localization of ezrin were frequently seen in the cervical cancers compared with the normal counterparts. Furthermore, this strongly positive ezrin expression was significantly higher in cervical cancers than in CIN, CGIN, and normal cervical epithelia. Ezrin overexpression was closely related with poor differentiation, late stage, and lymph node metastasis. Additionally, ezrin overexpression was associated with lower 10-year survival rate for patients with early stage cervical cancer, but not for patients with advanced stage.
Conclusions: Aberrant localization and overexpression of ezrin might be an independent effective biomarker for prognostic evaluation of cervical cancers.
Figures

References
-
- Li Q, Gao H, Xu H, Wang X, Pan Y, Hao F, Qiu X, Stoecker M, Wang E, Wang E. Expression of Ezrin correlates with malignant phenotype of lung cancer, and in vitro knockdown of Ezrin reverses the aggressive biological behavior of lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2012;33(5):1493–504. - PubMed
-
- Huang HY, Li CF, Fang FM, Tsai JW, Li SH, Lee YT, Wei HM. Prognostic implication of Ezrin overexpression in myxofibrosarcomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(12):3212–3219. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher A, Edwards K, Fehon RG. ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(8):586–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

