Neurotransmitter release: the last millisecond in the life of a synaptic vesicle
- PMID: 24183019
- PMCID: PMC3866025
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.10.022
Neurotransmitter release: the last millisecond in the life of a synaptic vesicle
Abstract
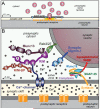
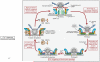
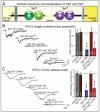
During an action potential, Ca(2+) entering a presynaptic terminal triggers synaptic vesicle exocytosis and neurotransmitter release in less than a millisecond. How does Ca(2+) stimulate release so rapidly and precisely? Work over the last decades revealed that Ca(2+) binding to synaptotagmin triggers release by stimulating synaptotagmin binding to a core fusion machinery composed of SNARE and SM proteins that mediates membrane fusion during exocytosis. Complexin adaptor proteins assist synaptotagmin by activating and clamping this core fusion machinery. Synaptic vesicles containing synaptotagmin are positioned at the active zone, the site of vesicle fusion, by a protein complex containing RIM proteins. RIM proteins activate docking and priming of synaptic vesicles and simultaneously recruit Ca(2+) channels to active zones, thereby connecting in a single complex primed synaptic vesicles to Ca(2+) channels. This architecture allows direct flow of Ca(2+) ions from Ca(2+) channels to synaptotagmin, which then triggers fusion, thus mediating tight millisecond coupling of an action potential to neurotransmitter release.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Augustin I, Rosenmund C, Südhof TC, Brose N. Munc-13 is essential for fusion competence of glutamatergic synaptic vesicles. Nature. 1999;400:457–461. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MK, Calakos N, Scheller RH. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992;257:255–259. - PubMed
-
- Brose N, Petrenko AG, Südhof TC, Jahn R. Synaptotagmin: A Ca2+ sensor on the synaptic vesicle surface. Science. 1992;256:1021–1025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

