Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health
- PMID: 24183105
- PMCID: PMC3988259
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61613-X
Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health
Abstract
Noise is pervasive in everyday life and can cause both auditory and non-auditory health effects. Noise-induced hearing loss remains highly prevalent in occupational settings, and is increasingly caused by social noise exposure (eg, through personal music players). Our understanding of molecular mechanisms involved in noise-induced hair-cell and nerve damage has substantially increased, and preventive and therapeutic drugs will probably become available within 10 years. Evidence of the non-auditory effects of environmental noise exposure on public health is growing. Observational and experimental studies have shown that noise exposure leads to annoyance, disturbs sleep and causes daytime sleepiness, affects patient outcomes and staff performance in hospitals, increases the occurrence of hypertension and cardiovascular disease, and impairs cognitive performance in schoolchildren. In this Review, we stress the importance of adequate noise prevention and mitigation strategies for public health.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

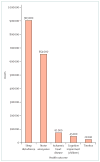
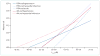
Comment in
-
Sound advice for public health.Lancet. 2014 Apr 12;383(9925):1270. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60631-0. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24725561 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hughes RW, Jones DM. Indispensable benefits and unavoidable costs of unattended sound for cognitive functioning. Noise Health. 2003;6:63–76. - PubMed
-
- Stansfeld S, Haines M, Brown B. Noise and health in the urban environment. Rev Environ Health. 2000;15:43–82. - PubMed
-
- Muzet A. Environmental noise, sleep and health. Sleep Med Rev. 2007;11:135–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

