Methamphetamine-associated memory is regulated by a writer and an eraser of permissive histone methylation
- PMID: 24183790
- PMCID: PMC4024089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.09.014
Methamphetamine-associated memory is regulated by a writer and an eraser of permissive histone methylation
Abstract
Background: Memories associated with drugs of abuse, such as methamphetamine (METH), increase relapse vulnerability to substance use disorder by triggering craving. The nucleus accumbens (NAc) is essential to these drug-associated memories, but underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Posttranslational chromatin modifications, such as histone methylation, modulate gene transcription; thus, we investigated the role of the associated epigenetic modifiers in METH-associated memory.
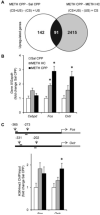
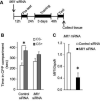
Methods: Conditioned place preference was used to assess the epigenetic landscape in the NAc supporting METH-associated memory (n = 79). The impact of histone methylation (H3K4me2/3) on the formation and expression of METH-associated memory was determined by focal, intra-NAc knockdown (KD) of a writer, the methyltransferase mixed-lineage leukemia 1 (Mll1) (n = 26), and an eraser, the histone lysine (K)-specific demethylase 5C (Kdm5c) (n = 38), of H3K4me2/3.
Results: A survey of chromatin modifications in the NAc of animals forming a METH-associated memory revealed the global induction of several modifications associated with active transcription. This correlated with a pattern of gene activation, as revealed by microarray analysis, including upregulation of oxytocin receptor (Oxtr) and FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene (Fos), the promoters of which also had increased H3K4me3. KD of Mll1 reduced H3K4me3, Fos and Oxtr levels and disrupted METH-associated memory. KD of Kdm5c resulted in hypermethylation of H3K4 and prevented the expression of METH-associated memory.
Conclusions: The development and expression of METH-associated memory are supported by regulation of H3K4me2/3 levels by MLL1 and KDM5C, respectively, in the NAc. These data indicate that permissive histone methylation, and the associated epigenetic writers and erasers, represent potential targets for the treatment of substance abuse relapse, a psychiatric condition perpetuated by unwanted associative memories.
Keywords: Demethylase; KDM5C; MLL; epigenetics; methyltransferase; nucleus accumbens.
© 2013 Society of Biological Psychiatry Published by Society of Biological Psychiatry All rights reserved.
Figures
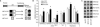

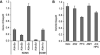

Similar articles
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broad domains of histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation are associated with transcriptional activation in CA1 neurons of the hippocampus during memory formation.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019 May;161:149-157. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.04.009. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019. PMID: 31002880 Free PMC article.
-
Methamphetamine causes differential alterations in gene expression and patterns of histone acetylation/hypoacetylation in the rat nucleus accumbens.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034236. Epub 2012 Mar 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22470541 Free PMC article.
-
miR-193a targets MLL1 mRNA and drastically decreases MLL1 protein production: Ectopic expression of the miRNA aberrantly lowers H3K4me3 content of the chromatin and hampers cell proliferation and viability.Gene. 2019 Jul 15;705:22-35. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.04.046. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31005612
-
MLL translocations, histone modifications and leukaemia stem-cell development.Nat Rev Cancer. 2007 Nov;7(11):823-33. doi: 10.1038/nrc2253. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17957188 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Landscape of Methamphetamine Use Disorder.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(12):2060-2066. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210524111915. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34030618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Effects of Nrf2 in Exercise Intervention of Neurotoxicity Caused by Methamphetamine Oxidative Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 18;2022:4445734. doi: 10.1155/2022/4445734. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35480870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroepigenetics and addiction.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;148:747-765. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-64076-5.00048-X. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29478612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulatory Dynamics in Models of Methamphetamine-Use Disorder.Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;12(10):1614. doi: 10.3390/genes12101614. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone modifications in cocaine, methamphetamine and opioids.Heliyon. 2023 May 19;9(6):e16407. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16407. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37265630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Milton AL, Everitt BJ. The persistence of maladaptive memory: addiction, drug memories and anti-relapse treatments. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012;36:1119–1139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

