Synaptic plasticity in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission following chronic memantine treatment in an in vitro model of limbic epileptogenesis
- PMID: 24184417
- PMCID: PMC3880158
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.10.016
Synaptic plasticity in glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission following chronic memantine treatment in an in vitro model of limbic epileptogenesis
Abstract
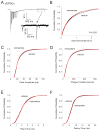
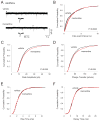
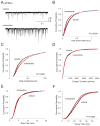
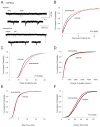
Chronic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) blockade with high affinity competitive and uncompetitive antagonists can lead to seizure exacerbation, presumably due to an imbalance in glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission. Acute administration of the moderate affinity NMDAR antagonist memantine in vivo has been associated with pro- and anticonvulsive properties. Chronic treatment with memantine can exacerbate seizures. Therefore, we hypothesized that chronic memantine treatment would increase glutamatergic and decrease GABAergic transmission, similar to high affinity competitive and uncompetitive antagonists. To test this hypothesis, organotypic hippocampal slice culture were treated for 17-21 days with memantine and then subjected to electrophysiological recordings. Whole-cell recordings from dentate granule cells revealed that chronic memantine treatment slightly, but significantly increased sEPSC frequency, mEPSC amplitude and mEPSC charge transfer, consistent with minimally increased glutamatergic transmission. Chronic memantine treatment also increased both sIPSC and mIPSC frequency and amplitude, suggestive of increased GABAergic transmission. Results suggest that a simple imbalance between glutamatergic and GABAergic neurotransmission may not underlie memantine's ictogenic properties. That said, glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission were assayed independently of one another in the current study. More complex interactions between glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission may prevail under conditions of intact circuitry.
Keywords: 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione; BMI; CNQX; D(−)-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid; D-APV; Dentate granule cell; Electrophysiology; GABA; Hippocampus; N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors; NMDAR; PSC; RMP; Resting membrane potential; SEM; Slice culture; TTX; aCSF; artificial cerebrospinal fluid; bicuculline methiodide; large amplitude spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current; mEPSC; mIPSC; miniature excitatory postsynaptic current; miniature inhibitory postsynaptic current; postsynaptic current; resting membrane potential; sEPSC; sEPSC(large); sEPSC(small); sIPSC; small amplitude spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current; spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current; spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic current; standard error of the mean; tetrodotoxin; γ-aminobutyric acid.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Aracava Y, Pereira EF, Maelicke A, Albuquerque EX. Memantine blocks alpha7* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors more potently than n-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;312:1195–1205. - PubMed
-
- Bausch SB. Organotypic hippocampal slice cultures as a model of limbic epileptogenesis. In: Baraban SC, editor. Neuromethods: Innovations in Epilepsy Research (Neuromethods) 40. Humana Press; New York: 2009. pp. 183–201.
-
- Bausch SB, He S, Petrova Y, Wang XM, McNamara JO. Plasticity of both excitatory and inhibitory synapses is associated with seizures induced by removal of chronic blockade of activity in cultured hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 2006;96:2151–2167. - PubMed
-
- Bausch SB, McNamara JO. Contributions of mossy fiber and CA1 pyramidal cell sprouting to dentate granule cell hyperexcitability in kainic acid-treated hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurophysiol. 2004;92:3582–3595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

