RNA-mediated gene activation
- PMID: 24185374
- PMCID: PMC3928182
- DOI: 10.4161/epi.26942
RNA-mediated gene activation
Abstract
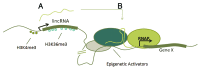
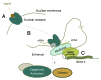
The regulation of gene expression by non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) has become a new paradigm in biology. RNA-mediated gene silencing pathways have been studied extensively, revealing diverse epigenetic and posttranscriptional mechanisms. In contrast, the roles of ncRNAs in activating gene expression remains poorly understood. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge of gene activation by small RNAs, long non-coding RNAs, and enhancer-derived RNAs, with an emphasis on epigenetic mechanisms.
Keywords: RNAa; eRNA; enhancer; epigenetic; lincRNA; non-coding RNA; saRNA; transcriptional activation.
Figures

References
-
- Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough J, Frith MC, Maeda N, Oyama R, Ravasi T, Lenhard B, Wells C, et al. FANTOM Consortium. RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group and Genome Science Group (Genome Network Project Core Group) The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science. 2005;309:1559–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1112014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
