Assessment of transcript reconstruction methods for RNA-seq
- PMID: 24185837
- PMCID: PMC3851240
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.2714
Assessment of transcript reconstruction methods for RNA-seq
Abstract
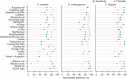
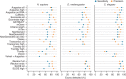
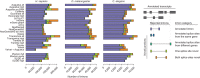
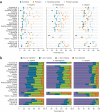
We evaluated 25 protocol variants of 14 independent computational methods for exon identification, transcript reconstruction and expression-level quantification from RNA-seq data. Our results show that most algorithms are able to identify discrete transcript components with high success rates but that assembly of complete isoform structures poses a major challenge even when all constituent elements are identified. Expression-level estimates also varied widely across methods, even when based on similar transcript models. Consequently, the complexity of higher eukaryotic genomes imposes severe limitations on transcript recall and splice product discrimination that are likely to remain limiting factors for the analysis of current-generation RNA-seq data.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Genomics: the state of the art in RNA-seq analysis.Nat Methods. 2013 Dec;10(12):1165-6. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2735. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 24296473 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

