Specific discrimination of three pathogenic Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serotypes by carB-based oligonucleotide microarray
- PMID: 24185846
- PMCID: PMC3911022
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02978-13
Specific discrimination of three pathogenic Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serotypes by carB-based oligonucleotide microarray
Abstract
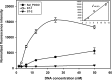
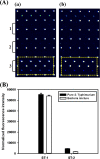
It is important to rapidly and selectively detect and analyze pathogenic Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica in contaminated food to reduce the morbidity and mortality of Salmonella infection and to guarantee food safety. In the present work, we developed an oligonucleotide microarray containing duplicate specific capture probes based on the carB gene, which encodes the carbamoyl phosphate synthetase large subunit, as a competent biomarker evaluated by genetic analysis to selectively and efficiently detect and discriminate three S. enterica subsp. enterica serotypes: Choleraesuis, Enteritidis, and Typhimurium. Using the developed microarray system, three serotype targets were successfully analyzed in a range as low as 1.6 to 3.1 nM and were specifically discriminated from each other without nonspecific signals. In addition, the constructed microarray did not have cross-reactivity with other common pathogenic bacteria and even enabled the clear discrimination of the target Salmonella serotype from a bacterial mixture. Therefore, these results demonstrated that our novel carB-based oligonucleotide microarray can be used as an effective and specific detection system for S. enterica subsp. enterica serotypes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of an oligonucleotide microarray method for Salmonella serotyping.Microb Biotechnol. 2008 Nov;1(6):513-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7915.2008.00053.x. Epub 2008 Aug 4. Microb Biotechnol. 2008. PMID: 21261872 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Salmonella enterica subpopulations by phenotype microarray antibiotic resistance patterns.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Dec;73(23):7753-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01228-07. Epub 2007 Oct 26. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17965201 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic chip-based detection and intraspecies strain discrimination of Salmonella serovars derived from whole blood of septic mice.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013 Apr;79(7):2302-11. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03882-12. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23354710 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence, distribution, and molecular and phenotypic characteristics of Salmonella enterica serotype 4,5,12:i:-.Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009 May;6(4):407-15. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2008.0213. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2009. PMID: 19292687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella enterica serotype Choleraesuis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical disease, and treatment.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004 Apr;17(2):311-22. doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.2.311-322.2004. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15084503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplex 16S rRNA-derived geno-biochip for detection of 16 bacterial pathogens from contaminated foods.Biotechnol J. 2016 Nov;11(11):1405-1414. doi: 10.1002/biot.201600043. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Biotechnol J. 2016. PMID: 27492058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Voetsch AC, Van Gilder TJ, Angulo FJ, Farley MM, Shallow S, Marcus R, Cieslak PR, Deneen VC, Tauxe RV, Emerging Infections Program FoodNet Working Group 2004. FoodNet estimate of the burden of illness caused by nontyphoidal Salmonella infections in the United States. Clin. Infect. Dis. 38:S127–S134. 10.1086/381578 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

